What is an API (Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient)?
An active pharmaceutical ingredient, abbreviated as API, is a substance used to produce a pharmaceutical product. API’s can have a direct impact on an indication. The active pharmaceutical ingredients or substances can eventually be converted into a drug or medicine.
The pharmacological activity of any API plays a direct role in the diagnosis, mitigation, cure, treatment, and disease prevention. API’s affect the structure and the functioning of the human body.
Medicines or pharmaceutical compounds all have inactive ingredients that are referred to as bulk pharmaceutical chemicals (BPCs).

Image Source: © Kalkine Group 2020
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), API is-

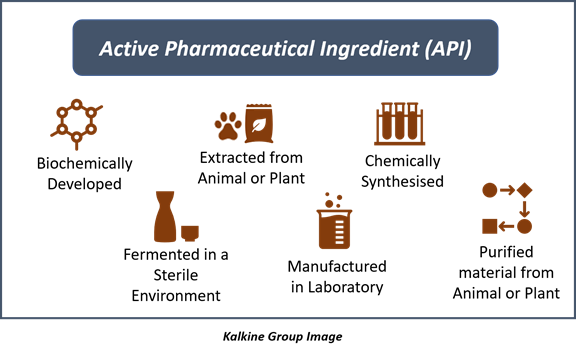
Categories of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
Active pharmaceutical ingredients are categorised into three main classes-
- Synthetic APIs- The synthetic APIs are directly obtained by chemical conversions methods.
- Semi-synthetic APIs- The semi-synthetic APIs are derived from the natural sources and then synthetically converted into the final product.
- Natural APIs- These are directly derived or extracted from natural sources (plants or animals).
What is the strength of an API?
The manufacturers or pharmaceutical companies use some standards for the determination of API’s strength in each drug. However, this standard could differ widely from brand to brand as there are several test methods to determine the strength of an API.
In all cases, developers have to prove their products’ potency to the Food Drug and Administration (FDA) in real-life patients, along with in the laboratory.
What is the Difference Between API and Inactive Ingredients?
An API and inactive ingredients together form a pharmaceutical product or drug. The difference between the two is in the respective roles and functionality of the two components.
The active ingredient is that part of a drug that has a medicinal effect on the body against a disease. In other words, it is a chemical entity that is responsible for the treatment of a specific disease.
Alternatively, inactive ingredients, sometimes termed as excipients, are the non-medicinal parts of a medicine. These ingredients do not have any pharmacological impact on the human body.
What is the difference between an API and an FFP?
It is essential to know that once an API is mixed with an excipient or some other API, it cannot be termed an API anymore. The blending is considered a part of
Finished pharmaceutical product (FPP) refers to the actual finalised medicine meant for the treatment of any disease. Finished dosage forms could be in several formulations, comprising tablets or capsules, syrup, a liquid solution, or any other. The finished dosage forms contain an active pharmaceutical ingredient with several inactive ingredients.
What is the role of Inactive Ingredients?
The inactive ingredients do not have any medicinal or therapeutic values on the human body. However, they are considered to be necessary components of most of the medicines. Inactive ingredients are the additional components to make up the composition of the drug with no effect on the body.
The inactive ingredients are also an important part in a medicine because they might be added in a pharmaceutical composition for several reasons.
Below mentioned are some reasons why inactive ingredients may be used in a drug or pharmaceutical formulation or medicine-
- Used as binding agents and buffers.
- Inactive ingredients act as fillers, especially if the API alone cannot be developed as a capsule, pill, or tablet.
- In some medicines, these are used as stabilisers for APIs.
- Inactive ingredients can be added as preservatives and to flavour the drug or add colour to it.
- These are also responsible for the effective absorption of a drug in the body.
- As a disintegrant, inactive ingredients help the medicine break up at the appropriate time.
- Inactive ingredients can also be used as coating agents for capsules, pills, and tablets to make them easy to swallow up.
Are there any regulatory requirements for APIs?
Most of the active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), as well as inactive ingredients used in medicine, are meant for the treatment of disease or patients use. Hence, manufacturers, distributors, including the entire supply chain are required to maintain high standards set out by the regulatory agencies.
There are some GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices) regulations for the manufacturing and development of APIs. The regulatory agencies make sure that APIs comply with all the requirements for purity as well as quality that they intend or are represented to retain.
The pharmaceutical companies or manufacturers of API must give detailed information about the manufacturing of the active ingredients.
There are some specific manufacturing requirements required to be followed by the manufacturer depending on the type of manufacturing process.
 Please wait processing your request...
Please wait processing your request...