What is an asset class?
An asset class refers to a set of financial instruments that display similar characteristics and are subject to the same rules and legalities. Asset classes constitute a collection of securities that manifest similar behaviour in the marketplace. Some examples of asset class include cash and cash equivalents, Equities (stocks), real estate, fixed-income investments (bonds), tangible assets, other financial derivatives, and futures. Usually, there is little correlation between the different classes of assets. To help investors diversify their portfolios, financial advisors focus on the asset class.
Summary
- An asset class refers to a set of financial instruments that display similar characteristics and are subject to the same rules and legalities.
- Some examples of asset class include cash and cash equivalents, Equities (stocks), real estate, fixed-income investments (bonds), and others.
- Asset classes constitute a collection of securities that manifest similar behaviour in the marketplace.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the impact of portfolio diversification on returns from investments?

Image Source: © 8vfand | Megapixl.com
Simply speaking, an asset class is a collection of comparable financial instruments. For instance, AAPL, IBM, and MSFT are a collection of stocks. There is, in some cases, a negative correlation between different classes of assets. This characteristic is vital for investing purposes.
Traditionally, Cash equivalents, equities (stocks), and fixed income (bonds) are considered the three main asset classes. At present, most financial advisors and investment professionals acknowledge even cryptocurrencies, other than real estate, other financial derivatives, commodities, and futures as the asset class mix. As we know, investment assets consist of both tangible and intangible securities that investors trade to generate extra income on a short-term or long-term basis.
Moreover, investment vehicles are seen as asset class categories by the investment professionals for diversification. Besides, each asset class involves different risks and offers different returns on investments. Further, each category of assets class performs differently in any given market environment. Therefore, to maximise returns from investments, investors mainly reduce portfolio risk via diversification of asset class.
Investment advisors emphasise asset class as a method to help investors diversify their investment portfolios. Every asset class involves different cash flows streams. Consequently, investing in various asset classes guarantees a certain amount of diversity in investment choices. Diversification lessens an investor's risk and increases their chance of making a good return.
What role does asset class play in investment strategies?

Image Source: © Josepalbert13 | Megapixl.com
What are the different kinds of asset classes?
Liquid asset classes such as equities (stocks), money market funds, bonds (fixed-income securities), cash, futures, commodities, and marketable securities are the most quoted asset classes. Liquid assets are those assets that can easily be converted into cash sans any loss in their value. At the same time, there are also other asset classes -- real estate and valuable inventory or stock such as tradable collectibles, stamps, and artwork. In addition, investment in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, crowdsourcing, hedge funds, venture capital is also considered a form of alternative investments by some analysts. The analysts believe that an asset's illiquidity does not represent its return potential; however, it only suggests that it may take more time to find a customer to convert the asset into cash.
As we know, alpha refers to the excess returns generated from an investment. Since portfolio diversification reduces unsystematic risks, investors or portfolio managers seeking alpha employ investment strategies to achieve alpha returns. It is to be noted that alpha gauges the value of an investment or portfolio relative to a benchmark or market index. Furthermore, investment strategies can focus on growth, income, value, or several other factors that help to identify and classify investment options according to a particular set of criteria. Some financial analysts relate criteria to performance/valuation metrics like the earnings-per-share (EPS) growth or the price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio. At the same time, some analysts are not concerned with the performance metrics but are more concerned with the asset class or the asset type. An investment in a specific asset class refers to an investment in that asset that displays a specific set of characteristics. Therefore, investments in the same asset class tend to have the same cash flows.
Historically, which asset class is believed to have offered the best returns?
For a very long time now, the stock market has proved to produce the highest returns compared to other investments. Since 1920, the compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) for the stock market index S&P 500 is around 7.63%, assuming that all dividends were reinvested and adjusted for inflation. This means that hundred dollars invested by an investor in the S&P 500 in January 1920 would have been worth about $167,983 (in 1920 dollars) by the year 2020. If we assume that inflation was not adjusted, the annual rate of return (ARR) will be 10.46%, and the total worth would have grown as huge as $2.3 million; however, if the same $100 invested in 10-year Treasuries would have been worth only a little over $8,000.
What are the four popular asset classes?
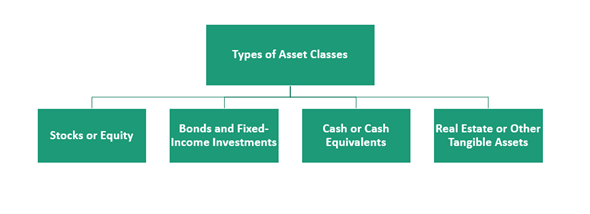
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
Equity - Equity represents shares of ownership. The shares issued by public-traded companies are traded on stock exchanges like New York Stock Exchange or NASDAQ. When someone buys shares in a company, they are purchasing ownership in that company. For instance, if company XYZ has 100,000 shares and an investor purchase 1,000, they will own 1% of Company XYZ. As such as part-owner, the investor will have rights to a portion of a company's profits, which the investor will receive from the company in the form of dividends. The dividend amount is not the same and differs from one company to another. Some companies might prefer to use the dividends to reinvest back into the company to achieve higher growth.
Nevertheless, the same investing principle does not apply to all companies. This implies that investing in a blue-chip stock that has been around for several years is different from investing in a hyper-growth startup. Besides often, the asset class of equities is subdivided into small-cap, mid-cap, and large-cap stocks.
Bonds and fixed-income investments – Fixed-income investments refer to investments in debt securities. The debt securities provide a return in the form of fixed interest payments. Investments in a fixed-income security are usually considered less risky as compared to investments in equities or other asset classes.
Cash or cash equivalents, like the money market funds – The primary advantage of cash or cash equivalent investments, also called money market instruments, is their liquidity. Cash equivalents like treasury bills, commercial papers are highly liquidity instruments. Money kept in the form of cash, or cash equivalents, is easily accessible.
Real estate or other physical assets – Real estate and other tangible assets are deemed an asset class that protects against inflation. Physical assets have a finite value and are considered more of a "real asset."
 Please wait processing your request...
Please wait processing your request...