What is Back testing?
Back testing is a technique that analyses the models or strategies in terms of their performance. Generally, the viability of a strategy is assessed in back testing by analysing its performance using historical data. If positive results are observed after back testing, then analysts and traders gain the confidence to employ it. The success of a strategy or model is assessed by analysing and predicting its capabilities.
Summary
- Back testing is a technique that analyses the models or strategies in terms of their performance.
- The viability of a strategy is assessed in back testing by analysing its historical performance using appropriate data.
- The success of a strategy or model is assessed by analysing predicting the capabilities of models or strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How back testing works?
Analysts or traders employ back testing methodology to test and compare a range of trading strategies or techniques before risking their funds. The back testing works on the theory that if a strategy has given poor results in the past, then it is highly unlikely that the same strategy will provide positive results in the future. While employing back testing, analysts mainly focus on the risk level and the profitability.
A back testing will consider a range of factors while measuring the performance of a strategy. A strategy will be marked successful when positive results are observed on the historical data. The back testing is employed with the assumption that the stock market follows the historical patterns.
To illustrate, a trader assesses a model to predict the future return on a stock. By utilising historical data, the new model is tested and results are achieved. After that, the analyst compares the results achieved from back test with the actual historical results. If any deviation is observed in the results, then the model will be tagged as not efficient for the future market.
Who employs back testing?
Back test can be performed by any individual but generally, it is employed by money managers and institutional investors. It is not used by individuals as it requires an abundance of historical data and it can be an expensive affair to get access to the data for complex modelling.
Financial capital and human capital are necessary for investment companies and institutional traders to use back testing techniques in their strategies. Since the stock market involves huge investments, then it is necessary for the institutional investors to employ back tests and reduce the risk.
How are back tests implemented?
Usually, the programmers code the back test and afterwards a simulation is run on the trading models or strategies. The simulation is run by employing historical data from bonds, stocks, or financial instruments. The analyst will assess the return from different models in different data sets after running back test.
To achieve reliable and valid results, it is suggested that models are tested in different market conditions. Moreover, the variables can be tweaked against different back testing measures.

What is the importance of back testing?
For developing an effective and efficient trading system, back testing is a crucial component. It is accomplished by testing the models or strategies on historical data or assessing the trades that might have taken place in the past based on the rules stated by the strategy in question. The results are used to determine the effectiveness of the strategy.
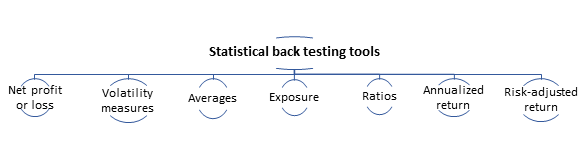
What are the statistical back testing tools?
Back testing can provide statistical feedback for a stated strategy or system. The universal statistical back testing tools are –
- Net profit or loss – it highlights the net gain or loss achieved by the strategy.
- Volatility measures – it projects the percentage change in the prices, either maximum downside or upside.
- Averages – The averages include the average loss, gains or bars held.
- Exposure – It indicates the number of funds exposed to the market risk or uncertainties.
- Ratios – Range of ratios depict the win or lose situation of an analyst.
- Annualized return – It stands for the annual return on the investment.
- Risk-adjusted return – It is the percentage of return for the risk taken.
What are the limitations of back testing?
To gain meaningful results from the back testing, a trader or analyst should develop a strategy that is not biased and tested in good faith. Chiefly, a strategy should not rely completely on the data used for performing the back test.
Generally, a strategy is constructed on the basis of the historical data set, therefore, a trader or analyst should ensure that the strategy constructed is tested on different data sets. If the same data set is used for back testing, then the results achieved will show positive results, however, the results will be meaningless in the future market.
Moreover, a trader should not do data dredging, that is, using the same data set to test numerous strategies. As it may produce results that seem positive but cannot be implemented in the current market.
To avoid data dredging, an analyst can employ different data sets for in sample and out of sample time period. In case, different results are achieved then the strategy can be seen as valid or successful.
What are the rules for employing back testing strategies?
- The broad market trends of a specified time frame should be considered while testing a strategy.
- The universe (for example, the test is limited to the tech stocks and does not consider other sectors) should be considered while undertaking back testing.
- While developing a trading system, the volatility factor should be considered as it plays a crucial role.
- While developing a trading system, the average number of bars held should be considered along with the commission costs.
- The exposure should be given due consideration as it is a double-edged sword. It is recommended to have 70% exposure to control the risk factor.
- The average profit or loss statists should be combined with the win to loss ratios as it can be helpful in ascertaining the optimal position sizing.
- Along with the annualized returns, the analysts should also take into consideration the decreasing or increasing risk factor. It can be achieved by using risk adjusted
- In some cases, the back testing conditions are tuned too much for the past and the results are not feasible for the future market.
- Back testing might not give an accurate result as the strategies which might be giving positive results in the past, might be proven useless in future.
 Please wait processing your request...
Please wait processing your request...