What is a brokerage company?
A brokerage company sells and buys bonds, stocks, options, and other financial goods on behalf of clients. Brokerages sometimes hire individual brokers to pool resources and provide the best service. Many financial services organisations also offer brokerage houses as part of their broader offerings.
Summary
- To facilitate a transaction, a brokerage company operates as a mediator to link sellers and purchasers.
- A percentage of the transaction amount or a flat charge is the most common commissions received by brokerage firms.
- Brokerage firms come in various shapes and sizes, offering multiple services and products at different prices and fees.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What does a "brokerage firm" operate?
A brokerage firm operates as a go-between, bringing buyers and sellers together to complete a transaction. Brokerage firms usually are compensated by commissions or fees charged after a transaction has been completed successfully.
Many discount brokerages have implemented zero-commission trading to compensate for the revenue loss in other ways, such as receiving payment from the exchanges for more significant volumes of order flow. When a trade order for a stock is performed, an investor pays a transaction fee for the brokerage company's efforts to complete the trade.

Source: © Denisismagilov | Megapixl.com
There would be no need for brokerage firms in a perfect market, where everyone had access to all available information and could act on it correctly and rapidly. However, there is no such thing as perfect information, asymmetric knowledge, or opacity in reality. As a result, customers are often unaware of the sellers and offer the most excellent deal. Likewise, sellers are in the same boat as buyers.
Brokerage firms exist to assist their clients by matching the opposite side of a trade, bringing sellers and purchasers together at the best feasible price for each, and charging a fee for their services.
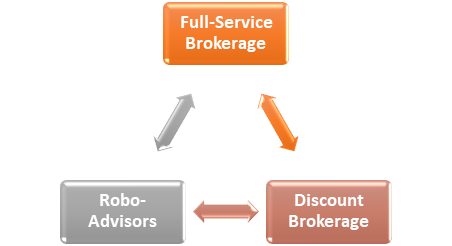
What kind of brokerage businesses are there?
Full-Service Brokerage
Estate planning, money management, financial counselling, and tax counselling are among the services and products offered by full-service brokerages, often known as traditional brokerages.
These firms also provide economic research, real-time stock prices, and market analysis. They employ highly skilled financial counsellors and professional brokers who create connections with their clients. Traditional brokerages charge a fee in addition to a commission.
Discount Brokerage
A discount brokerage is less expensive than a full-service advisor. Still, it may offer fewer finished goods and services and lack the personal relationship development that a full-service advisor provides. An investor's account size frequently determines the quality and breadth of discount brokers' advice.
Several full-service firms also have a low-cost discount brokerage division. These firms charge cheaper commissions by using computerised trading systems and requiring their clients to undertake their research, which can be done online or via a mobile app.

Source: © Convisum | Megapixl.com
Robo-Advisors
Robo-advisors, who have been around since the 2010s, is a type of digital-only online investment platform that uses algorithms to execute trading strategies on behalf of clients in an automated manner. Most robo-advisors adhere to modern portfolio theory (MPT) principles by investing in long-term passive index strategies. At the same time, some now allow customers to tweak their investment approach if they prefer more active management.
The draw of robo-advisors is not only the automation but also the low starting account balances and costs. In many situations, robo-advisors charge no commissions, have no annual fee and can begin with as little as a few dollars.
Some robo-advisers are now employing human advisors who can engage with customers. However, these advisors are rarely able to alter the recommended portfolio allocation generated by their algorithms.
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
What is the function of a brokerage firm?
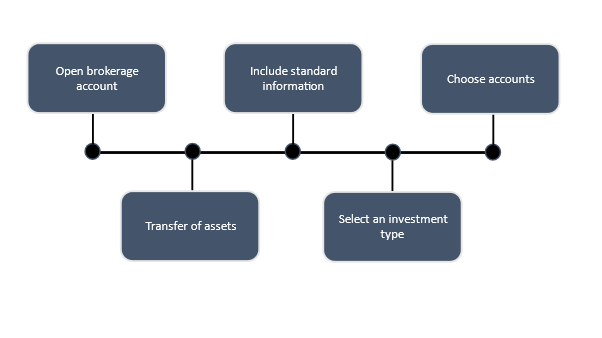
Here's how a brokerage firm operates.
- Registering for a brokerage account.
- Include standard information such as your contact information, name, and bank account number.
- Choose between retirement accounts, nonretirement accounts, health savings accounts, and college savings accounts when opening an account.
- Use a bank transfer or a transfer of assets from another brokerage business to fund the account.
- Select an investment type, such as bonds, stocks, exchange-traded funds, or mutual funds.
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
What is the difference between independent and captive brokerage?
Brokers aren't just for investing; they also work in the insurance industry. When working with insurance brokers, there are two sorts of agents: captive and independent. Here's a quick overview of each.
Captive Agents
Captive agents work for only one insurance firm, and many of them are well knowledgeable about the company's services and products. Because they work for the same insurance business, these agents may develop ties with corporate staff and underwriters.
Independent Agents
Individual agents, sometimes known as independent agents, choose to work with various insurance firms rather than being committed to one. These agents have agreements with these businesses and are authorised to sell their goods. Some independent agents may charge a fee to individuals.
 Please wait processing your request...
Please wait processing your request...