What is Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC)?
A central Bank Digital currency (CBDC) is the digital form of a nation's currency backed by the trust of its regulating government. It is usually under the control of any country's central bank, backed by national governments. The concept is of a new type of currency and is still in developmental stages worldwide. CBDCs are based on blockchain technology and the same underlying principles as cryptocurrencies. Countries around the world are experimenting with it. Some ambitious and tech-pro countries, like China and South Korea, have already finished the demo and pilot testing for their CBDCs.
Summary
- CBDC is the digital form of a nation's currency backed by the trust from its regulating government.
- No nation has launched its CBDC yet, but a lot of them are developing such models.
- Any CBDC would essentially work on blockchain principles and Distributed ledger technology.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)-
What are the key features of CBDC?
- Most CBDCs should have these characteristics:
- It should essentially work on Blockchain and Distributed Ledger technology.
- The CBDC must be available for unrestricted, public use like any other currency in use.
- It should be recognised as a legal tender by the Central Banks or the country's Apex Bank.
- There should be a degree of anonymity in the currency, like Cryptocurrency.
- Its back end system should be operationally available 24 hours a day and seven days a week.
- The Central Bank must directly guarantee the at-par convertibility of CBDC into cash and/or reserves.
- Digital currency may be allowed to take different forms based on payment infrastructure technology available.
- The CBDC may be subjected to an interest rate on CBDC liabilities by the central bank. The rate shall be consistent with the interest rate structure in the country's monetary policy.
- It should enable governments with easy payment tracking while ensuring privacy.

Image Source: © Kdrs32 | Megapixl.com
Which technologies back CBDC?
Though government backed and centralised, CBDC uses blockchain technology like other available decentralised virtual currencies. Being government backed, CBDC needs to keep a record of all transactions by every entity on a centralised database. After all, digital fiat currencies or CBDC will act as a digital representation of a country's fiat currency. It will also be backed by a suitable amount of monetary reserves like gold or foreign currency reserves. This is why a shared or distributed ledger system becomes essential for the central banks before launching a CBDC. It is a reason why several nations are still testing the implementation and design of CBDC. UK, Sweden, China, Venezuela have already launched experiments with or without blockchain technology.
As per the Bank of England's illustrative model of CBDC, it would work in the following way-
CBDC model mechanism
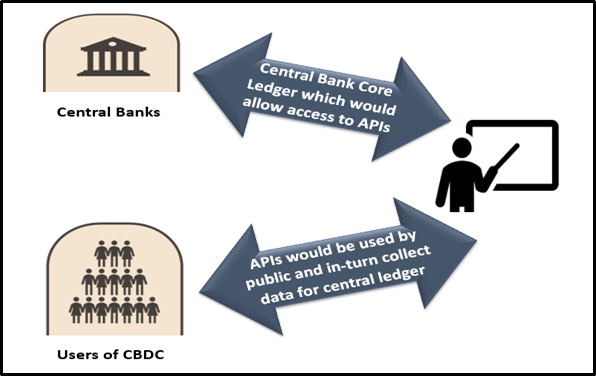
Image Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
The Central bank would provide a secure, resilient platform for the CBDC and a core ledger functionality as per the above model. It would give access to Authorised Payment Intermediaries (APIs) to connect to the core ledger. The APIs would develop interfaces for users, which would be compatible with computers, mobiles or cards. Registered users with the APIs would then be able to use the CBDC for transactions.
What are the advantages CBDCs will bring?
- CBDCs have the potential to improve the speed of transactions.
- It is a cost-efficient method for governments.
- It may also help to overcome security faults in the current banking system.
- CBDCs would be a much resilient approach towards currencies.
- It will save on paper and metals used for printing and minting notes and coins.
- CBDCs can reduce operational risks in the banking
- All transactions would have traceability.
- The possibility of black money and unauthorised money printing would vanish.
How is a CBDC different from any Cryptocurrency?
Though CBDC and Cryptocurrencies both work on similar backend technologies, there are still a few differences.
- The supply of Cryptocurrency is not as regulated as it is expected for CBDC. CBDC supply would be regulated similarly to any other nation's currency. In contrast, cryptocurrency supply is often fixed to regulate price movements.
- CBDC would have a central entity managing its distributed ledger. While in the case of Cryptocurrency, anyone is allowed to run the software without permission.
- CBDCs would work under a structured approach, while cryptocurrencies do not have any such structure. It is a major reason for the crypto-trading volatility.
- Transferring money using Cryptocurrency is still not accepted by most nations around the world. It would not be the same with CBDC, which would have government backing and permission.
- Tracking payments of Cryptocurrency is only possible for an individual himself/ herself. In the case of CBDC, transactions would be highly transparent and regulated.
- The taxation system on cryptocurrency transactions is still not evolving; it has many loopholes. In the case of CBDC, the government would not lose any revenue.
What are the currently known types of CBDC?
CBDC can be either wholesale or retail, based on its purpose.
- A Wholesale CBDC can be exchanged between private central banks. It enables streamlining payments between financial institutions, cross-border transactions. Wholesale CBDC works to replace a banks' reserve deposits with digital tokens. Governments worldwide have high hopes with wholesale CBDC to make international transactions cheaper, faster, and safer.
- Retail CBDC, on the other hand, is the digital money used by an average person for day to day transactions. Retail CBDC renders cash obsolete, alongside increase the efficiency, traceability and transparency of payments.
There are two known systems using which central banks are seeking to roll out CBDC.
- Token-based system- The CBDC under this system is created as a token with a precise denomination. Any transfer of the CBDC token for payment would only transfer a token from one party to another. It would not require matching two databases but would just be an immediate transfer of ownership. It would work like a transfer of a banknote from one person to another.
- Account-based system- In this kind of CBDC rollout, the central bank would keep accounts of the users of CBDC. It is a cumbersome approach as the central bank would have to open and manage individual accounts alone or through other regulated banks. With every transfer detail regarding it, this kind of CBDC would reach the central bank, like any other bank transfer now.
 Please wait processing your request...
Please wait processing your request...