Cloud computing is the distribution of a range of computing services via the internet. The computing services include servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics, among others. Cloud computing is an extremely popular and widely used technology. Some of the major players in the industry include Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, and IBM Cloud.
The best part of using cloud computing services is that it is helpful in reducing the operating cost. At the same time, it is swift, provides flexible resources and offers the advantage of economies of scale.
Cloud Computing
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is the distribution of a range of computing services via the internet. The computing services include servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics, among others. Cloud computing is an extremely popular and widely used technology. Some of the major players in the industry include Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, and IBM Cloud.
The best part of using cloud computing services is that it is helpful in reducing the operating cost. At the same time, it is swift, provides flexible resources and offers the advantage of economies of scale.
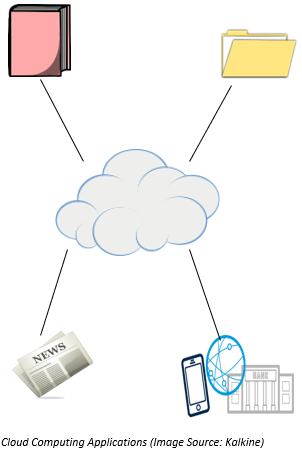
As highlighted in the image above, through cloud computing, it is possible to read a newspaper, do net banking, read books, save files and many more.
After having some idea about cloud computing, let us also understand some of the benefits of cloud computing.
GOOD READ: 3 Stocks to Leverage the Cloud Computing Boom in 2020
What are the Benefits of Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing can be considered as a significant transition from the traditional working style. Below are some of the reasons why most companies are switching to the cloud.
Reduces Operating Cost:
One of the major advantages of cloud computing is that it saves a lot of money. People do not have to worry about purchasing hardware to save any file. Different software is also available through the cloud. Thus, it reduces additional cost purchasing software.
Cloud Computing is highly elastic:
Probably the biggest advantage of cloud computing is its elasticity. In essence, it means providing the required computing power, storage, and bandwidth at any point of time from any geographical location.
Supports Business Continuity:
Cloud computing has a critical role to play at the time of any disaster. For any business, protecting data and system is critical during a BCP (business continuity plan) situation. Whatever be the situation, with cloud computing, one can be sure that their data are safe and secure.
Supports Collaboration Within Organization:
When the resources are available on the cloud, the employee would be able to access the files, communicate with each other, even while sitting at different corners of the world.
Automatic Updates:
Users of cloud computing services usually receive automatic updates related to the software. In case one has a software on one’s device connected to the cloud, and there is an update on the software, one would also be eligible for automatic software upgrade depending on the software fees.
Security:
Various cloud providers are offering a set of policies, technologies, and controls capable of strengthening the security of your data, files, applications, plus an infrastructure to safeguard from external threat.
How Many Types of Cloud Computing are there?
There are different types of clouds catering to varying needs of the end-users. There are several models, solutions, types, and services that have grown with time and that match the specific needs of the user.
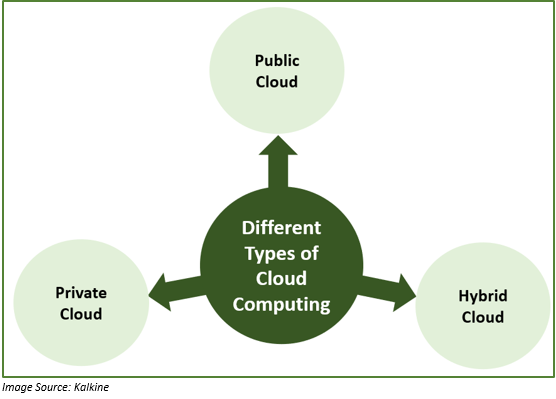
Let us discuss the three types of cloud computing.
Public Cloud:
Public clouds are owned and controlled by third-party cloud service players. These providers offer services like servers and storage over the internet. An example of Public cloud is Microsoft Azure. With the public cloud, the entire hardware, software, and other supporting infrastructure are owned by the cloud provider. The services on the public cloud can be accessed via a web browser.
Private Cloud:
In a private cloud, the resources on the cloud can be accessed entirely by a single company. This private cloud could be situated on the company’s on-site data center. In some cases, these companies provide third-party service providers to manage their private cloud.
Hybrid Cloud:
Hybrid cloud, as the name indicates, is the amalgamation of both the private and public cloud. In Hybrid cloud, the two are bound together via a technology that enables data and applications to be shared. With data free to move between the two clouds, there exists more flexibility within the business and more deployment options, thus, helping to optimize the prevailing infrastructure, security, and compliance.
What are the different types of Cloud Computing Models?
Cloud computing has three types of models. Each model signifies a different component of the cloud computing stack.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS):
Infrastructure as a Service comprises of the basic building blocks for cloud IT, and it gives access to network features, computer, and data storage spaces. This cloud model provides its user with the highest level of elasticity and management control over the IT resources.
Platform as a Service (PaaS):
Platform as a Service model eliminates the need for a company to manage the underlying infrastructure. It supports its users to concentrate on the implementation as well as the management of their applications. The advantage of using this model is that the user need not have to think about purchasing any resource, capacity planning, software maintenance that is needed to run the application.
Software as a Service (SaaS):
Software as a service model gives the user a complete product that is operated and managed by the service provider. In most cases, people refer to SaaS as an end-user application. Through this SaaS model, the user gets relieved from the tension of maintaining the service and management of underlying infrastructure. The SaaS user only has to think about different ways to use a particular application. An example of SaaS is an email one sends to another person without worrying about how the application is operating at the back-end.
Cloud Computing Outlook
Cloud computing has massive scope for the future. Its role was significant during the pandemic when most people switched to remote working. Market experts believe that cloud computing will grow at a considerable pace. According to some research reports, the cloud computing market is expected to grow at a CAGR in the late teens and exceed US$800 million in size by 2025.
Existing Market Dynamics:
- Improved return on investment at a lower infrastructure and storage cost.
- Existing requirement to handle regulatory and compliance policy needs.
- Increase in the adoption of hybrid cloud service.
- Cloud computing experiences challenges of cyber-attacks impacting businesses.
INTERESTING READ: 5G, Cloud Computing, Bundling – the three pieces of pie in Australian Telecom
Uses of Cloud Computing
Most things have gone online in the present times, and people are using online mode to watch movies, play games, listen to music, and many more. This is possible because of cloud computing. From the smallest companies to the biggest in the world, all are utilizing this technology for several purposes. In this section, we would look at a couple of applications of cloud computing.
- Cloud is used for building, deploying, and scaling applications at a faster rate.
- Cloud is used to reduce the application cost and time via cloud infrastructures that can be easily scaled up or down as per the requirement.
- Through cloud computing, a user can protect data in a cost-effective way and on a massive scale. It also transfers the data to an offsite cloud storage system that can be assessed from any place and device.
- Cloud is used for consolidating data across teams, units, and locations. Different people can then assess these data to uncover insights for more informed decisions.
- Cloud computing is used to connect people from any location, at any time and any device with high-definition audio and video features with global distribution.
- Users use intelligent models to engage clients and offer them valuable understandings from the data taken.
- We often get software update notifications. Cloud computing provides users with software updates providing the latest versions and updates as per their requirement.
Drawbacks of Cloud Computing
So far, we have seen the features and benefits of cloud computing. But at the same time, we cannot ignore that it has its drawbacks. Let us look at some of them.
- One of the biggest disadvantages of the technology is the risk of data confidentiality as multiple people can access the data.
- Cloud computing works when there is an internet connection. In the absence of the internet, or if the internet path to the cloud has some disturbance, access to cloud computing machine would be complicated.
- As everyone can access the public cloud, there is a probability of data getting hacked. Data being highly confidential, businesses cannot afford any leakage of sensitive data.
- When we store data on the cloud, we depend on a third party to take care of our data. We become dependent on the data center of the provider.
- In case someone experiences some technical challenges, he/she has no option to rectify from their end. Instead, they have to connect with the hosted provider’s technical support team for help.
- Cloud computing technology does not work well in case the connection is low.
- Every cloud provider differs from one another. Hence, it may be possible that the users may not get the same features. Some providers offer limited versions and allow the most popular features only, while some do not provide features and customization as per the user’s demand.
As highlighted in the image above, through cloud computing, it is possible to read a newspaper, do net banking, read books, save files and many more.
After having some idea about cloud computing, let us also understand some of the benefits of cloud computing.
GOOD READ: 3 Stocks to Leverage the Cloud Computing Boom in 2020
What are the Benefits of Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing can be considered as a significant transition from the traditional working style. Below are some of the reasons why most companies are switching to the cloud.
Reduces Operating Cost:
One of the major advantages of cloud computing is that it saves a lot of money. People do not have to worry about purchasing hardware to save any file. Different software is also available through the cloud. Thus, it reduces additional cost purchasing software.
Cloud Computing is highly elastic:
Probably the biggest advantage of cloud computing is its elasticity. In essence, it means providing the required computing power, storage, and bandwidth at any point of time from any geographical location.
Supports Business Continuity:
Cloud computing has a critical role to play at the time of any disaster. For any business, protecting data and system is critical during a BCP (business continuity plan) situation. Whatever be the situation, with cloud computing, one can be sure that their data are safe and secure.
Supports Collaboration Within Organization:
When the resources are available on the cloud, the employee would be able to access the files, communicate with each other, even while sitting at different corners of the world.
Automatic Updates:
Users of cloud computing services usually receive automatic updates related to the software. In case one has a software on one’s device connected to the cloud, and there is an update on the software, one would also be eligible for automatic software upgrade depending on the software fees.
Security:
Various cloud providers are offering a set of policies, technologies, and controls capable of strengthening the security of your data, files, applications, plus an infrastructure to safeguard from external threat.
How Many Types of Cloud Computing are there?
There are different types of clouds catering to varying needs of the end-users. There are several models, solutions, types, and services that have grown with time and that match the specific needs of the user.
Let us discuss the three types of cloud computing.
Public Cloud:
Public clouds are owned and controlled by third-party cloud service players. These providers offer services like servers and storage over the internet. An example of Public cloud is Microsoft Azure. With the public cloud, the entire hardware, software, and other supporting infrastructure are owned by the cloud provider. The services on the public cloud can be accessed via a web browser.
Private Cloud:
In a private cloud, the resources on the cloud can be accessed entirely by a single company. This private cloud could be situated on the company’s on-site data center. In some cases, these companies provide third-party service providers to manage their private cloud.
Hybrid Cloud:
Hybrid cloud, as the name indicates, is the amalgamation of both the private and public cloud. In Hybrid cloud, the two are bound together via a technology that enables data and applications to be shared. With data free to move between the two clouds, there exists more flexibility within the business and more deployment options, thus, helping to optimize the prevailing infrastructure, security, and compliance.
What are the different types of Cloud Computing Models?
Cloud computing has three types of models. Each model signifies a different component of the cloud computing stack.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS):
Infrastructure as a Service comprises of the basic building blocks for cloud IT, and it gives access to network features, computer, and data storage spaces. This cloud model provides its user with the highest level of elasticity and management control over the IT resources.
Platform as a Service (PaaS):
Platform as a Service model eliminates the need for a company to manage the underlying infrastructure. It supports its users to concentrate on the implementation as well as the management of their applications. The advantage of using this model is that the user need not have to think about purchasing any resource, capacity planning, software maintenance that is needed to run the application.
Software as a Service (SaaS):
Software as a service model gives the user a complete product that is operated and managed by the service provider. In most cases, people refer to SaaS as an end-user application. Through this SaaS model, the user gets relieved from the tension of maintaining the service and management of underlying infrastructure. The SaaS user only has to think about different ways to use a particular application. An example of SaaS is an email one sends to another person without worrying about how the application is operating at the back-end.
Cloud Computing Outlook
Cloud computing has massive scope for the future. Its role was significant during the pandemic when most people switched to remote working. Market experts believe that cloud computing will grow at a considerable pace. According to some research reports, the cloud computing market is expected to grow at a CAGR in the late teens and exceed US$800 million in size by 2025.
Existing Market Dynamics:
- Improved return on investment at a lower infrastructure and storage cost.
- Existing requirement to handle regulatory and compliance policy needs.
- Increase in the adoption of hybrid cloud service.
- Cloud computing experiences challenges of cyber-attacks impacting businesses.
INTERESTING READ: 5G, Cloud Computing, Bundling – the three pieces of pie in Australian Telecom
Uses of Cloud Computing
Most things have gone online in the present times, and people are using online mode to watch movies, play games, listen to music, and many more. This is possible because of cloud computing. From the smallest companies to the biggest in the world, all are utilizing this technology for several purposes. In this section, we would look at a couple of applications of cloud computing.
- Cloud is used for building, deploying, and scaling applications at a faster rate.
- Cloud is used to reduce the application cost and time via cloud infrastructures that can be easily scaled up or down as per the requirement.
- Through cloud computing, a user can protect data in a cost-effective way and on a massive scale. It also transfers the data to an offsite cloud storage system that can be assessed from any place and device.
- Cloud is used for consolidating data across teams, units, and locations. Different people can then assess these data to uncover insights for more informed decisions.
- Cloud computing is used to connect people from any location, at any time and any device with high-definition audio and video features with global distribution.
- Users use intelligent models to engage clients and offer them valuable understandings from the data taken.
- We often get software update notifications. Cloud computing provides users with software updates providing the latest versions and updates as per their requirement.
Drawbacks of Cloud Computing
So far, we have seen the features and benefits of cloud computing. But at the same time, we cannot ignore that it has its drawbacks. Let us look at some of them.
- One of the biggest disadvantages of the technology is the risk of data confidentiality as multiple people can access the data.
- Cloud computing works when there is an internet connection. In the absence of the internet, or if the internet path to the cloud has some disturbance, access to cloud computing machine would be complicated.
- As everyone can access the public cloud, there is a probability of data getting hacked. Data being highly confidential, businesses cannot afford any leakage of sensitive data.
- When we store data on the cloud, we depend on a third party to take care of our data. We become dependent on the data center of the provider.
- In case someone experiences some technical challenges, he/she has no option to rectify from their end. Instead, they have to connect with the hosted provider’s technical support team for help.
- Cloud computing technology does not work well in case the connection is low.
- Every cloud provider differs from one another. Hence, it may be possible that the users may not get the same features. Some providers offer limited versions and allow the most popular features only, while some do not provide features and customization as per the user’s demand.
 Please wait processing your request...
Please wait processing your request...