What is Cryptojacking?
Cryptojacking is a malicious activity where cybercriminals hack into personal computers and business computers by installing a software. Cryptojacking is also known as Illicit cryptocurrency mining. The software code is easy to deploy and runs in the background of computer systems, making it difficult to detect. The software drains the computer battery at a faster rate, causes delays in computer response time, high electricity bills, overheating of the device, and increased processor usage.
With a few lines of code, the hacker can get access to the victim’s cryptocurrency wallet and use the resources for cryptocurrency mining (crypto mining). The cybercriminals drain the earned currency or steal it by transferring them to their wallets through the seized computers.
If the cryptocurrency wallet is compromised, the owner will not be able to recover the amount. Whereas, in the case of bank accounts, the stolen amount is transferred back by the bank.
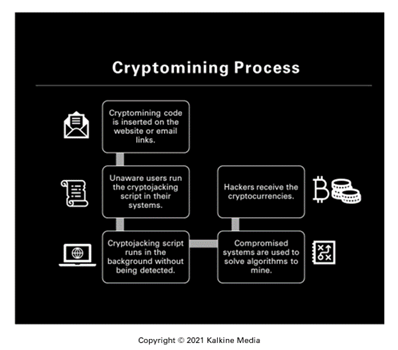
How do cryptojackers spread cryptojacking scripts?
Cryptojackers can use any of these methods to perform crypto mining maliciously:
- File-based: The cryptojacking file is downloaded, and it spreads the script to the entire computer system. The most common medium through which crypto mining scripts are downloaded is via emails. The hackers send this email with an attachment, which seems legitimate to the user, and the user downloads it. Once the file gets downloaded, the crypto mining script runs in the system's background without the user being aware of it.
- Browser-based: The hackers build a mining script and insert it into advertisements and in vulnerable and outdated plugins available on numerous websites. The script runs automatically with the code being downloaded to the user’s computer.
Cryptojacking can also occur through third-party attacks or supply-chain attacks. For instance, the hacker can install the mining scripts along with the relevant banking information to have all the proceeds saved in their wallets. This primarily happens when the website is poorly secured.
- Cloud-based: The hackers search through an organization's files and look for application performing interface (API) keys to access all the organization’s servers or cloud services. Post gaining access, hackers can draw resources from unlimited computer systems resulting in substantial account losses. This method accelerates the illegal mining of a currency.
Summary
- Cryptojacking is a malicious activity where cybercriminals hack into personal computers and business computers by installing a software
- If the cryptocurrency wallet is compromised, the amount cannot be recovered unlike in bank accounts
- Methods used by cryptojackers for illicit mining include executing mining scripts, hijacking the IT system or through a cloud service
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- How to prevent the IT infrastructure from being subjected to cryptojacking?
The preventive measures essential to protect the computer systems, servers, and crypto assets that could be compromised by cryptojacking are:
- The IT team should clearly understand and be trained on concepts of cryptojacking. The team should be educated to detect the hijacking of the IT systems and be ready to take the necessary action steps.
- It is imperative to educate employees against cybercrimes. It is required that they be taught not to click on any links available in emails or websites that may execute a cryptojacking code, download the required files only from trusted websites, and reach out to the IT team if facing any slowness or overheating.
- It should be suggested to the computer user that they enable the extensions to block browser-based cryptominers using extensions like minerBlock, Anti Miner, and No Coin.
- Web advertisements are the most common medium for crypto mining scripts to get executed in the system. To detect and block these scripts from being executed, it should be suggested that ad-blockers be used.
- Disabling JavaScript can also play a vital role in preventing computers and servers from getting infected with malicious code. Upon disabling, it will also block many of the functions used while browsing.
- Why are cold wallets safer than hot wallets?
Digital wallets (also known as cryptocurrency wallets) are the wallet holder's financial account used to store funds, make transactions, and maintain transaction history. Cold wallets store cryptocurrency on the offline platform and protect the wallet from cryptojacking or any other vulnerabilities. A cold wallet is considered safer because it is not connected to the internet, making it susceptible.
On the contrary, hot wallets are connected to the internet facilitating the transfer of crypto assets and securities. When compared to a cold wallet, hot wallets are riskier. Examples of a few cold wallets are Ledger Nano X, Trezor Model T, Ledger Nano S, etc.
- When did the first cryptojacking happen?
The first cryptojacking case showed up in September 2017 at Coinhive. With the launch of Coinhive, there was a rise in browser-based cybercrime rather than file-based cryptojacking. With the help of its ready-made scripts, cryptojacking was made more accessible as it did not require downloading a file into the victim's system.
The organization published a mining code for owners to earn a passive income on their websites. Hackers realized that this code could mine their currency using a website’s visitors' resources. This code used the visitor’s computer to mine, and this continued for as long as the web page was open. Coinhive was shut in 2019.
- Could mobile phones also be hacked to perform mining?
Cryptojacking affects mobile devices along with other traditional devices like personal computers and laptops. Mobile cryptojacking occurs when users unintentionally download fraudulent applications seeking financial and personal information or through web pages. Mobile cryptojacking can hamper device performance and affects network bandwidth.
In 2018, Apple came up with restrictions on crypto mining to diminish the increasing threats to iOS. To prevent cryptojacking on mobile devices, a strong mobile device management solution is required.
 Please wait processing your request...
Please wait processing your request...