What is debt financing?
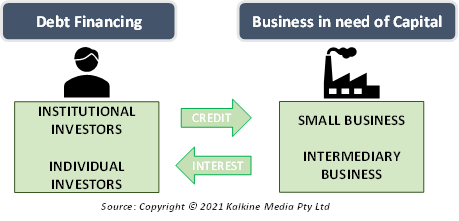
Debt financing refers to the process of procuring capital to conduct business operations through the sale of bonds, bills, or notes. The investors who fund these businesses include institutional investors as well as individuals. However, the money received by a business must be paid back to these investors. Hence the name “debt financing” is given to this type of business financing.
The lender receives the loan amount as well as interest over it. Debt financing is a method to bring in capital in the early stages of a business. Debt financing is one of the two methods used by businesses to raise money, the other method being equity financing.
Under debt financing, the owners of the business can retain full ownership of their shares. Debt financing allows businesses to obtain money without having to sell equity.
Summary
- Debt financing is a method used by businesses to raise capital by selling debt instruments like bills, bonds, or notes.
- The money invested in these businesses must be paid back in full along with an additional interest amount.
- Debt financing is one of the two methods through which capital can be raised, the other one being equity financing under which investors are given shares of the company in exchange for their funds.
- Startups and small businesses often use debt financing to fund their operations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How does debt financing work?
The company uses debt instruments to raise capital. A business can issue a bond or a bill which the investor purchases. The investors purchasing this are either retail or institutional investors that provide the company with the required capital.
The borrower and lender both agree upon a date when the principal amount must be paid back along with interest payments. This is like buying a bond wherein the owner of the bond is promised interest payments and a full refund of face value on maturity. If the company goes bankrupt, lenders gain a claim on any liquidated assets over shareholders. Thus, shareholders are the last to be paid in such an event.
How is debt financing measured?
There are various tools involved in the process of debt financing. These are used to evaluate the health and viability of the companies. Some of the indicators used to evaluate the strength of a firm are:
- Cost of debt: Interest payments represent the true cost of taking over a debt. This is so because these interest payments are paid over and above the principal amount and increase the value of the loan. This interest is tax-deductible, making the effective cost of debt lower than that shown in the coupon rate. The cost of debt can be measured through the following formula:

This represents the effective cost of debt after subtracting the tax benefit.
- Debt-to-equity Ratio: Debt-to-equity ratio is often used by businesses to calculate the proportion of lender’s funds in the company to those of the shareholders. This is measured by considering the assets funded by these sources separately.
A low debt-to-equity ratio is preferable and signifies that the business does not have much liability in its balance sheet. On the other hand, if the ratio is too low then it could mean that the company is completely funded by shareholders who are not able to obtain profits. Thus, some amount of debt is necessary to ensure that the funds of shareholders do not get completely used up in financing the business. The ratio is given as follows:

- Interest Coverage Ratio: This ratio signifies the number of times earnings meet the interest expenses. Thus, it signifies the efficiency and profitability of the business. A high value of the ratio is ideal and is preferred by banks and lenders in extending loans.
It is given by the following formula:
What are the advantages of debt financing?
- Retention of ownership: Debt financing allows businesses to avoid the dilution of shares which happens in the case of equity financing. This would mean that the profits made by the business would go back to the business owners and would not have to be shared with outside shareholders.
- Tax-deductible interest: Interest payments are allowed as a deduction in the calculation of income. These help businesses save up on tax payments. Thus, debt financing might be a cheaper option than other firms of investing.
- Planning: This type of financing allows the owner to be sure of how much money would be required to be paid each month. Thus, budgeting becomes easier under debt financing.
What are the disadvantages of debt financing?
- Requirements: There are certain qualification criteria that needs to be met before businesses are eligible to get any kind of credit. This includes having a good credit rating. Thus, if a fresh business does not have any credit rating, then lenders may not be interested in funding them.
- Discipline: Monthly ineptest payments require a level of discipline to be met. Good financial sense is required to carry out debt financing.
- Collateral: When a lender asks for a collateral then that puts the asset put under collateral under potential threat. At times business owners may be asked to put their personal assets as collateral, potentially creating risk for the owner.

 Please wait processing your request...
Please wait processing your request...