What is the European Medicines Agency or EMA?
The EMA, or European Medicines Agency, is a decentralised organisation of EU (European Union). The agency is responsible for the scientific assessment, supervision, along with the safety monitoring of medicines in the EU. an independent Management Board regulates the EMA. The day-to-day operations of the agency are carried out by the EMA staff and supervised by its Executive Director.
EMA is a networking organisation of thousands of specialists from across Europe who carry out the work of scientific committees of the agency.
The European Medicines Agency has seven scientific committees to evaluate medicines along their lifecycle from initial stages of development, through marketing authorisation to safety monitoring once they are on the market. The seven committees include:

When any healthcare company wants to sell a drug in the EU, it must first seek clearance from the EMA. The EMA also assesses the drug’s safety after its approval, via pharmacovigilance.
The History of EMA
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) was established in 1995 and has worked throughout the European Union and across the world to safeguard human and animal health. The EMA evaluates drugs/medicines via stringent scientific standards and offers partners and shareholders science-based information on drugs/medicines.
EMA has a track record of over a quarter of a century of safeguarding the efficacy and safety of medicines for humans and animals across Europe. The agency also promotes research and innovation for the development of drugs.
With the foundation of the Committee for Orphan Medicinal Products (COMP) in 2000, EMA enhanced its services to patients and healthcare professionals (HCPs). The COMP is responsible for advising orphan drug designation to medicines which are for orphan or rare diseases.
What are the major roles of the EMA?
The EMA is accountable for the scientific assessment, mainly of innovative & high-technology drugs, that are manufactured by pharmaceutical companies for usage in the EU. The agency ensures the best use of scientific resources across Europe for the evaluation, supervision, and pharmacovigilance of medicines.
The EMA works to promote scientific superiority in the assessment and regulation of medicines, for human as well as animal health in the European Union (EU).
Facilitate medicine development and access
The agency is committed to enabling appropriate patient access to new drugs and has a vital role in providing support during medicine development for patients’ benefit. Medicine developers, who want to perform clinical trials in the EU, are required to submit applications to the national expert authorities of the countries where they wish to conduct clinical trials.
The EMA does not play a role in the clinical trials authorisation in the EU. The national competent authorities have the responsibility for the approval of the trials.
The European Medicines Agency also plays a critical role in supporting research and innovation in the pharmaceutical industry. The agency also promotes innovation & development of new medicines by European micro, small as well as medium-sized enterprises.
Evaluation of marketing authorisation applications and Medicine safety monitoring
The scientific committees of EMA give independent suggestions on medicines for human and veterinary use, based on thorough scientific evaluation of provided data.
The assessments of marketing-authorisation applications submitted via the centralised process offer the basis for the authorisation of medicines across Europe.
Provide information to healthcare professionals (HCPs) & patients
EMA publishes impartial and transparent information related to medicines and their approved applications. This comprises public versions of scientific evaluation reports and summaries written in layman language.
What is the European Medicines Regulatory Network?
The medicines regulating system in Europe is distinctive all over the world. The regulatory system is based on a synchronised regulatory network of the competent authorities in the European Economic Area’s Member States working jointly with the EMA and the European Commission.
The European medicines regulatory network is the keystone of the work and success of EMA.
By closely working together, this network makes sure that safe, effective, and superior-quality medicines are authorised throughout the EU.
The regulatory network also makes sure that the patients, HCPs, and citizens are provided with adequate and consistent medicines information.
Advantages of the European medicines regulatory network for EU citizens
- The network enables Member States to combine resources & manage work for regulating medicines efficiently & effectively.
- European medicines regulatory network establishes assurance for patients, HCPs, industry, along with governments by confirming consistent standards and best available expertise use.
- The network also reduces the administrative burden via the centralised authorisation procedure, which helps medicines to reach patients sooner.
- It accelerates the information exchange on essential issues related to the medicines’ safety.
How does the EMA authorise the medicines?
All medicines should be authorised before their marketing and before reaching to the patients. In the European Union, there are two main routes for approving medicines-
- Centralised route
- National route
Under the centralised authorisation procedure, the pharmaceutical companies submit a single marketing authorisation application (MAA) to the European Medicines Agency.
In the centralised authorisation process, healthcare companies required to submit a single marketing-authorisation application to the EMA. This permits the marketing authorisation holder to market the medicine. After approval of the application, the drug shall be available to the patients and HCPs via the EU based on a single marketing authorisation.
CHMP or CVMP committee of the EMA carry out a scientific evaluation of the application and provide advice on whether the drug should be marketed or not.
The below-represented image shows how the European Medicines Agency assesses medicines-
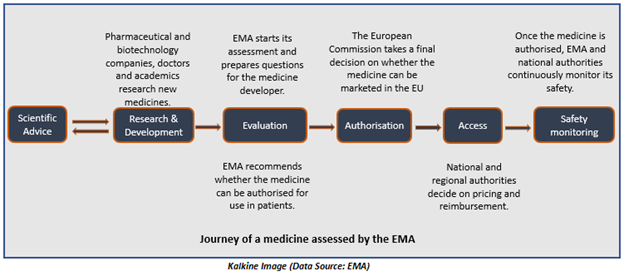
After receiving a grant by the European Commission, the centralised marketing authorisation of a drug becomes valid in the EU Member States and the European Economic Area nations including Liechtenstein, Norway, and Iceland.
Advantages of centralised authorisation process EU Citizens:

 Please wait processing your request...
Please wait processing your request...