What is the FDA?
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is the oldest and most comprehensive consumer protection agency in the United States federal government. The FDA is responsible for the protection of public health by guaranteeing the safety, efficacy, as well as security of human and veterinary drugs, biological products, medical devices, food supply, cosmetics, along with the products that emit radiation. Moreover, the agency also provides precise, science-based health information to the public.
FDA approval is relevant for investors, specifically those who are interested in healthcare companies (Pharmaceuticals and biotech players). Also, the approval process is essential primarily for those healthcare companies that are involved in the drug development process. Without an FDA approval, regulated products under the purview of FDA would not be issued for sale in the United States.
A look at the History of FDA
The FDA is the oldest consumer protection organization in the United States federal government. Since 1848 the US federal government has used chemical analysis for monitoring safety of agricultural products a responsibility inherited by the Agriculture Department in 1862 and later by the FDA. The regulatory functions of the FDA began with the 1906 clearance of the Pure Food and Drug Act.
Since then, the FDA has changed together with social, political, economic as well as legal modifications in the US. Examination of the history of these modifications explains the evolving role that the regulatory agency has played in encouraging public health.
What are the responsibilities of the FDA?
FDA has the responsibility of ensuring public health safety. The agency helps to protect public health by assuring food safety & quality, from electronic product radiation to regulating tobacco products.
The responsibilities of FDA extend to 50 Unites States including Puerto Rico, the Virgin Islands, the District of Columbia, Guam, American Samoa, and other territories & possessions in the United States.
A glance at the responsibilities of FDA-
- FDA maintains public health safety by assuring the safety of food poultry and some egg products.
- To make sure safety & effectiveness of human and veterinary drugs, vaccines & other biological products, and medical devices that are intended for human use.
- Protection of the public from electronic product radiations.
- Ensuring the cosmetics, as well as dietary supplements, are safe and labeled appropriately.
- Advancing public health by helping to fast-track product innovations.
What does FDA regulate?
FDA is accountable for upgrading human health & safety by boosting innovations that make medical products more effective, safer, as well as affordable.
The FDA is renowned for its work in regulating the development of innovative treatments. The FDA has established some rules concerning the clinical trials that must be completed on every new drug. Healthcare players must perform clinical trials before marketing of new drug into individuals.
To know more about clinical trials, click here.
Generally, FDA regulates foods, drugs, medical devices, biologics, electronic products that give off radiation, cosmetics, veterinary products, and tobacco products.
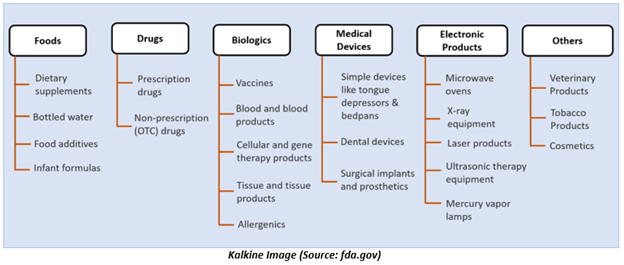
How Can FDA Approvals transform the fate of Healthcare companies?
Approval or rejection from the FDA for a new drug or sale of an existing drug in the United States can have a financial impact on any healthcare company. If the FDA approved any drug, it could drive an increase in the revenue of the company. The FDA also performs inspection animal testing facilities and clinical trials sites.
For small-cap companies that are developing a new drug, their fate depends on receiving approval from the regulatory authorities. Also, the market value of healthcare shares depends on the FDA approval process. The decision of the FDA might affect the stock market and give investors an idea about how the company is going to operate in the upcoming period.
To understand the impact of an FDA approval in a specific stock, click here.
How does the FDA drug approval process work?
- Drug development and animal testing- After manufacturing a new drug, the manufacturer or sponsor seek authorization by the FDA for commercialization in the US. The new drug must be assessed by the sponsor for toxicity in animals.
- Investigational New Drug (IND) Application and Review- After animal testing, the sponsor submits an investigational new drug application to the FDA based on the results from the initial testing. The initial experiments include the drug’s composition and manufacturing process. Based on these experiments, the sponsor develops a plan for testing the drug in clinical trials.
- FDA Approval to conduct clinical trials- Once the FDA approves the drug after reviewing its IND, the clinical trials of the drug are performed.
- Review meeting- The FDA meets with the drug manufacturer or sponsor before submission of a New Drug Application (NDA).
- NDA Application- The drug sponsor formally seeks advice from the FDA to approve the drug for marketing in the US by submitting an NDA. An NDA includes all animal and human information related to how the drug works in the body. It also comprises information about the manufacturing process of the drug.
- Review of Application- After receiving an NDA, the FDA has two months to decide whether to file it to review or not. Once the FDA files an NDA, a review team is assigned for evaluating the research on the safety and efficacy of the drug.
- Drug Labeling- Once the application is reviewed, the FDA also reviews the professional labeling & makes sure that appropriate information is communicated to the healthcare professionals.
- Facility Inspection- FDA examines the manufacturing facilities where the tested drug will be manufactured.
- FDA Drug Approval- After the entire review and inspection process, the FDA reviewers will approve the application of sponsor or provide a response letter, also known as a Complete Response Letter.
 Please wait processing your request...
Please wait processing your request...