What is Globalization?
Globalization has long been supported in view of the economic, political and cultural benefits, supporting the exchange of ideas, talent, technology, culture, trade and investment. However, the trending phenomenon of Globalization is under the scanner, with increasing difficulties faced by policymakers in preventing the national economic crisis and economic depression from creating havoc across the globe.
Be it 1930s Great Depression, 2008’s Global Financial Crisis or 2020’s Global Virus Crisis, Globalization has played a major role in the geographical spread of financial and economic turmoil.
Globalization is defined as a phenomenon of the world becoming interconnected by the exchange of goods, services, people, trade, culture, money, ideas, technology and policies. It refers to the interdependence of human resources, corporates and governments across the world. Though it has been taking place for hundreds of years, the Globalization process has expedited over the last half-century, encompassing economic, cultural and political exchanges across the globe.

How Do We Trace Back the Early Signs of Globalization?
In the history books, the inter-state trade has its mention from the earliest civilizations dating back to roughly 1600s. Communities and states enlarged interdependence equations and trade, resulting in key exchange of social ideas and practices. Back in the third millennium BC, the economic trades happened between Sumer and Indus Valley Civilisation with the commercial urban centres opening between the Greek to Indians. This inter-state trade phenomenon was not only driven by Europe but also Old World centres - India, China, Japan.
Further, free-trade agreements, global political and economic discussions, and free-flow of money, people and technology promoted the evolution of Globalization in different themes.
How Do We See Current Globalization Trends?
Since the beginning of the 19th century, Globalization has accelerated with the breakthrough in transportation and communication technology. In the late 20th and early 21st century, Globalization has also increased for the sports and entertainment sector.
Besides, digital trade as a component of Globalization is gaining importance between the nations. Investment flows for accessing new markets in developing economies and associated investment, people and technology flows also shape the growing Globalization trends.
Financial markets including commodity, debt, currency and stock markets are increasingly interconnected, with market players tapping buoyant investment opportunities across the world. On cultural exchanges, movement of students for academic purposes and learning is further supporting global interconnection trends.
Although Globalization is probably serving as a bridge between countries to create more wealth, studies have shown it is not reducing the economic gap between the poorest countries and the richest. Conflicts between nations and irregular diplomacy have played a large part in the history of Globalization, and it continues to do so.
What are the Key Drivers of Globalization?
Transportation: The speed, length and breadth of Globalization has increased for a number of reasons. Developments in Information Technology, transport and communication sectors have rapidly grown over the past 40 years. The internet has been transformative in closing the gap in communication with providing fast and 24/7 access world over. The containerization system where large quantity goods and commodities are shipped using intermodal containers has also enabled trade around the globe at extremely low cost.
Communications: The sharp rise in social and digital media has made the national boundaries absolutely irrelevant as any company can communicate and market its products and services in any part of the world directly connecting with its target audience. Easy access to virtual global market trade has grown substantially after the emergence of the internet. New electronic payment systems such as e-wallets, mobile banking, pre-pay have facilitated the increased global trade. For better or worse, globalised trade, supply chain, outsourcing have changed the way the world operates, and its impact on organizational operations and practices continues to grow.
Free trade: Following the collapse of communism ideology, the trade has become increasingly free with many former communist countries opening for Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and global trade. The emergence of global players such as Google, Facebook, Apple, Microsoft, etc are by-products of Globalization.
Is Globalization Changing the World for Better or Worse?
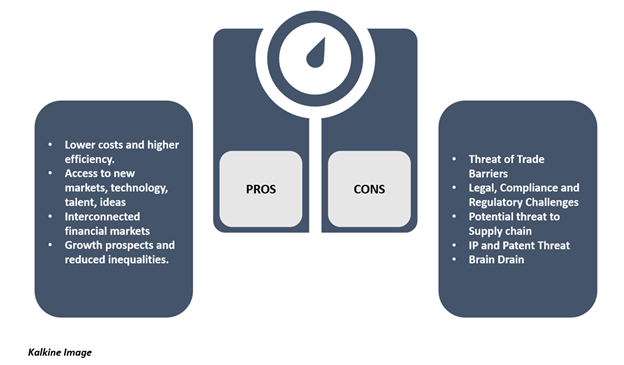
Globalization have several pros and cons attached to the international linkages between economies and markets. Current Globalization trends have largely integrated developing economies with less developed economies through Foreign Direct Investment (FDI); with the decrease in trade barriers like import quotas and tariffs as well as economic reforms like policies and regulations, and also at a large extent, immigration.
International standards have created efficiency in the trade for goods and services, and the International Organization sets these standards. Currently, the most significant free-trade area is the European Union. EU policies implement the free movement of resources (human, capital and ideas) within the European Union market. Access to broader markets means higher demand for products and services.
Though it can also lead to a lack of product diversity, like most of the world's computers, use Microsoft's Windows operating system, presenting barriers to small, local producers. Besides, global players are exerting downward pressure on wages below fair market equilibrium level.
How is Globalization Influencing Culture and Political behaviors?
At present, most of the cultures have been defused because of the internet, popular culture media and travel. As people are more exposed to other cultures, transition of ideas, values, meanings take place, which is also extended into fashion, food, languages and even religion. While Globalization’s impact on art and culture is clearly visible, but it also creates uncertainty in ideologies and disorientation in identities. Critics of Globalization argue that global connectivity poses thread to prevalent indigenous cultures.
Globalization has also interlinked state governments, intergovernmental organisations, social organisations etc. This integration between national and international levels of authority have pushed the emergent global political economy. Some countries also allow its citizens to take citizenship of other countries. Another essential aspect of Globalization is the movement of people, not only limited to immigrants but also encompassing movement for travel and business. Foreign students' revenue across different courses and learning programs add to country’s economic growth, both financially and culturally.
But overdependent on these interlinkages in terms of trade, money and culture can be harmful as the system may collapse when there is a sudden downturn in the world. Novel coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic completely halted peoples’ movement, which impacted tourism, education, hospitality industries severely.
 Please wait processing your request...
Please wait processing your request...