What is ideation?
Ideation is the process of generating ideas, which includes acquiring information and collecting thoughts about those ideas. Ideation can be applied to existing services or goods to improve them. As a result, it is a method of producing fresh concepts and ideas for future improvements.
From the original idea to implementation, it is helpful to describe thought sequences. Ideas can emerge from previous or current information, opinions, external influences, principles, or convictions. Ideation can be expressed orally, in writing, or graphically.
Summary
- The method of forming ideas from conception to implementation is known as ideation.
- Derivative ideas, solutions to problems, and symbiotic ideas are examples of ideation styles.
- Ideation can be expressed graphically, verbally, or in writing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
All You need to know about Ideation
In business, how does ideation work?
Ideation is a term used in the business world to describe the process of creating and communicating prescriptive ideas to others.
Anyone tangentially or directly linked with a company or organisation, including managers, low-level employees, partners, customers, and stakeholders, can contribute ideas and the act of ideation. Online forums, brainstorming sessions, team-building exercises, seminars, social media platforms, and surveys can lead to actual ideas.
Source: © Aiconimage | Megapixl.com
Ideation is a critical component of any globally successful firm. For example, Google used to encourage and motivate employees to spend up to 20% of their work time meditating on new ideas that piqued their interest and potentially solved real-world problems. Unfortunately, as the company has developed, it appears that this is not being used as often as it once was.
Companies can become more inventive or stay competitive by focusing on ideation, which increases the possibility of new product launches, higher customer acquisition, and improved financial performance.
Ideation can be applied externally as well as internally.
When ideation is performed externally, firms typically target their existing customer base. This is because they are more familiar with the company's product. After all, they utilise it. In addition, customers have the knowledge to supply firms with service/product enhancement ideas. Thus, this is where most external ideation efforts are concentrated.
In the internal use of ideation, businesses aim to acquire ideas from their employees who work on and create services and products. Internal ideation frequently involves collaborative activities like prototyping and brainstorming.

Source: © Dharshani | Megapixl.com
What is the real-world ideation process?
Although there is no single universal model for ideation, people can follow some broad rules to assist them in improving the effectiveness of ideation and the solutions it generates.
To begin with, ideation does not always start with a randomly produced notion; instead, ideas are reverse engineered to fit emergent situations. As a result, it is necessary first to define the problem and comprehend its significant underlying aspects, such as business settings, industry trends, budget restrictions, consumer expectations, and any other elements contributing to the troublesome issue at hand.
The variety of ideas developed during the cooperation stages is narrowed down to one dominant notion that will best guide the group's next actions. This marquis concept is put to the test against the problem and tweaked as necessary. It is then carefully rewritten, retested, and fine-tuned until a viable answer is found. The idea is next tested in the actual world, and if it proves to be a success, the ideation process is complete.
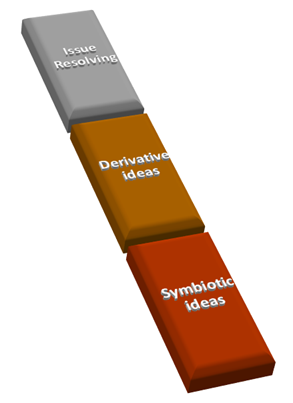
The following are examples of ideation styles:
- Issue solving is the easy method that entails a person identifying a problem and then resolving it.
- Modifications to an existing concept are referred to as derivative ideas.
- Symbiotic thoughts result from numerous unfinished concepts that come together to form a fully formed, holistic concept.
Source: Kalkine Media
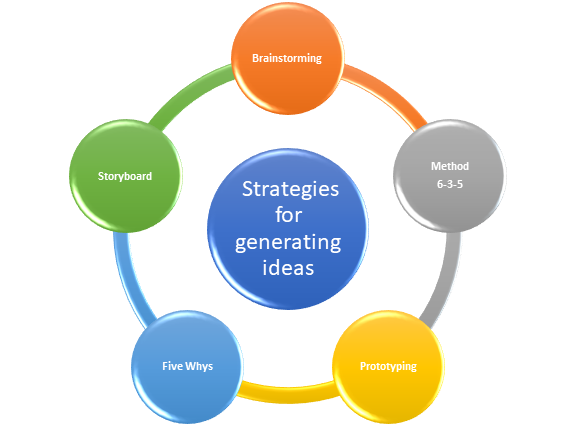
What are the most common strategies for generating ideas?
There are various methods for generating new ideas that require less time and money yet are nonetheless very successful. Here are some approaches for ideation that can be put to the test in the workplace.
Brainstorming
The purpose of the brainstorm is to use the group's collective intelligence to build on each other's ideas. It is one of the most well-known brainstorming approaches, and an activity to do at work.
The organisation can use this strategy to ensure that the team involved is varied while also limiting the brainstorm to five or seven people. This is because the smaller the group, the more effective and focused the discussion will be. In addition, this is because only the people the organisation requires will be present, and those employees will feel more responsible for coming up with new ideas because the crowd will not drown out their voices.
Method 6-3-5
Six people jot down three ideas in five minutes using the method 6-3-5 of brainstorming. When the five minutes are up, members of the team move their sheet to the next person so that their colleague can develop their thoughts. By democratising the process and putting each employee on an equal footing, this task is conducted in silence to prevent anyone from controlling the idea generation or discussion.
Source: Kalkine Media
Creating a prototype
Prototyping is a method of creating a tangible model of a concept, and it can be beneficial during the brainstorming process. In addition, employees can use prototyping to see how their product will perform and to receive input from external and internal stakeholders earlier in the development process.
Analysis of the Five Whys
The "Five Whys" methodology, in which employees are obliged to question "why" five times, was popularised by Toyota. The purpose of the exercise is to get to the bottom of the problem, which may entail asking one or 10 "whys."
Storyboard
Companies can use a storyboard to create visual storytelling about their issue or remedy. For example, the activity allows groups to depict their ideal customer and the scenarios in which they might interact with the company. In addition, storyboarding will enable teams to see challenges and forecast the effects of their solution in the future.
 Please wait processing your request...
Please wait processing your request...