“The theory of economics is a method rather than a doctrine, an apparatus of mind, a technique of thinking, which helps its possessor to draw correct conclusions”
- John Maynard Keynes
Macroeconomics Vs Microeconomics
Macroeconomics and microeconomics are the two major branches in economics. While microeconomics study individual behaviour and business decisions, macroeconomics take a top-down approach looking at the economy as a whole, trying to determine its course and nature.
Macroeconomics look at overall economic parameters at the broader level, including GDP, unemployment, inflation, growth rate, and analyse various decisions made by country and policymakers.
A key part of fundamental analysis for traders, corporations, governments and policymakers, macroeconomic indicators provide insight into the state of a country’s economy. They are a vital piece of economic data, often regarded as the silver bullet when one seeks to judge the overall health of an economy.
“Macroeconomics is the analysis of the economy as a whole, an examination of overall supply and demand. At the broadest level, macroeconomists want to understand why some countries grow faster than others and which government policies can help growth”- Alex Berenson, Prominent & Author.
What Are Macroeconomic Indicators?
As the name and its derivation suggests, macroeconomics (Greek prefix makro- meaning "large" and economics) refers to a branch of economics that deals with the performance, structure, behaviour, and decision-making of an economy as a whole. Hence, macroeconomic indicators can be described as statistics or readings that reveal the production or output of an economy, government, or sector. They are also referred to as fundamental data releases.
These are of utmost importance to analysts and governments as they help assess the current and future health of the economy and financial markets. So much so, macroeconomics has been regarded as an analytical tool, integral to craft economic and fiscal policy.
What Are Characteristics Of Macroeconomic Indicators?
Experts agree that macroeconomics as a field can be complicated, as several factors influence it. These factors are analysed with various economic indicators that tell us about the overall health of the economy. Macroeconomic indicators ideally demonstrate the following characteristics-
- They tend to vary in their meaning and the impact they have on the economy.
- These indicators may fluctuate in frequency.
- Market participants keep an eye on analysts’ predictions of the macroeconomic data ahead of their release.
- The health and state of these indicators depict the health of the economy and policy effectiveness.
- These indicators can have a significant influence on market movements.
- Changing market conditions can also affect the significance of a macroeconomic indicator.
- One cannot be certain that macroeconomic indicators are reliable on their own, but they sure have a role in shaping the economy.
What Are Key Macroeconomic Indicators?
Before we understand the major macroeconomic indicators, it should be noted that, there are two main types of indicators- leading indicators, which forecast where an economy might be heading and lagging indicators, which reflect an economy’s historical performance and only change after a trend has been established.
Macroeconomic Indicators encompass interest rates announcements, GDP, consumer price index, employment indicators, retail sales, monetary policy, and more.
Let us cast an eye on five key macroeconomic indicators -
- Gross Domestic Product- GDP is the monetary value of all finished goods and services produced in a country within a particular time period. The indicator helps in comparing the economies, forecast their growth and aid key policymaking decisions.
- Inflation Rate- Consumer Price Index or inflation refers to sustained increase in the prices of goods and services in a country, thereby exerting pressure on the purchasing power. During periods of economic growth, there is likely to be an increase in inflation, whereas episodes of economic downturn tend to see declining levels of inflation, or even ‘deflation’.
- Unemployment Rate- Labour market statistics are essential in understanding the economy’s overall growth. A lagging indicator, unemployment rate is the percent of the labour force that is jobless. It tends to rise or fall in the wake of changing economic conditions.
- Real Estate Market- House prices and overall housing market is a vital leading indicator, predicting about the state of the economy, months in advance. For instance, building permits can be a leading indicator of economic health, as businesses can grab the opportunity to apply for these permits.
- Interest rates- The interest rate is the per cent of principal charged by the lender for the use of its money. Interest rates are very competitive and impact the economy by controlling the money supply.
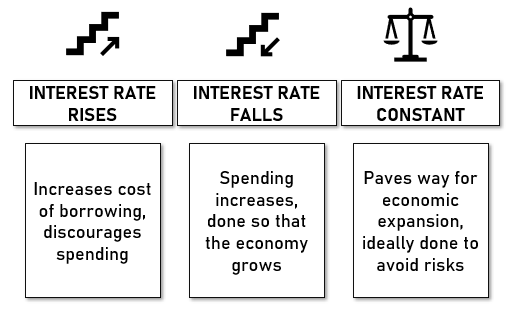
ALSO READ: Can Negative Interest Rates help Economies?
Did You Miss on These Macroeconomic Indicators?
The above discussed indicators are vital and common to most economies, but there are others that deserve equal attention-
- Stock market- Rise in stock market demonstrates confidence in the future of businesses, which could lead to economic growth. On the contrary, a dip in the market indicates that investors are taking their money out of shares and probably fleeing to safe-haven assets, amidst economic uncertainty.
- Production and manufacturing statistics- An increase in production and manufacturing output is likely to have a positive impact on GDP figures, which is a sign of increased consumption and positive economic growth.
- Retail sales- Consumerism accounts for a huge portion of economic activity. Retail sales have been considered as one of the extremely crucial macroeconomic indicators as they monitor purchases of finished goods and services by both consumers and businesses. It should be noted that increasing retail sales is an indication that the economy is improving.
- Currency strength- Another reflection of the health and stability of the economy, a currency’s price is believed to be based on how buyers and sellers perceive its value. Besides, the currency’s value reflects the political and economic circumstances of the economy as well.
MUST READ: 5 Factors to blame for Australian dollar plunge
What Is The Significance Of Analysing Macroeconomic Indicators?
Let us take an example to understand the importance of macroeconomic indicators. Suppose you wish to invest in a car. When the price of your favorite model goes up, it affects you.
But would you not wonder- why is the car suddenly expensive? Is demand greater than supply? Is the cost going up because the Company is using pricey raw materials ? Or, is market competition picking up steam and affecting the car’s price?
To answer these questions, we turn on to macroeconomic indicators, as they may explain the bigger picture of what’s currently happening in the economy for a product to be suddenly expensive (or vice-versa!).
Staying up to date with the stance of macroeconomic indicators helps one in decision making and even smart investing. One may see these as voluminous statistics, but they are key indicators for evaluating the health of the economy, the latest business cycles and understanding how consumers are spending.
ALSO READ: Recession, and how do we Measure it?
What Is The Link Between Macroeconomic Indicators And Equity Market?
Equity market and the economy appear to portray a bi-directional correlation. In general, mounting stock prices or a bull market tends to boost confidence in an economy, encouraging investment and stimulating further growth- a key trait of a healthier economy, in addition to overall stability and employment.
Besides, equity market participants are big consumers of macroeconomic data. Markets react promptly to any news- escalating political tensions, war and rumours of war, change in regulatory environment for business, interest rate fluctuations, unemployment and income stature.
Effective Market Hypothesis opines that stock price is a proficient market indicator, meaning that asset prices reflect all available information. However, the forward-looking stock market, also an indicator of economy, may decipher a trend that is different from that of economic health.
GOOD READ: Understand the Linkages between Economics and the Equity Market
Why Are Macroeconomic Indicators Important To Consider While Making Investments?
Macroeconomic indicators have been seen to be capable of driving the stock market into frenzy, causing a lot of money to be lost or made in a mere instant.
The stock market is considered to be a good predictive indicator of economic health. This is because market participants spend a fair amount of time assessing the health of companies and the economy in an attempt to make rational and prudent investment decisions.
Some experts even argue that stock prices are determined by fundamental macroeconomic variables. This makes one confident that macroeconomic indicators may influence investment decisions and even motivate researchers to investigate the relation between stock market prices and macroeconomic variables.
Should One Rely Solely On Macroeconomic Indicators While Investing?
Research suggests that economic factors tend to drive equity market movements to a significant extent, with GDP being a typical gauge of the market health. Some investors even consider GDP to be the holy grail of their investing decisions as it reveals all the facts about the economy, production, income, saving and investment.
However, it is worth noting that stock market is also driven by other variables such as political shocks, environmental factors and natural events, company fundamentals, regulatory policies, and investors’ expectation and sentiments.
Hence, a multitude of factors - both economic and non-economic, propel the health of equity markets.
 Please wait processing your request...
Please wait processing your request...