What is a New Chemical Entity or an NCE?
According to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), a new chemical entity (NCE) is a treatment that comprises no active entities that have been authorised by the FDA.
An NCE is a molecule developed by a pioneer company in the initial stage of drug discovery. After undertaking clinical studies, the NCE could convert into a drug used for the treatment for an indication.
The synthesis of an NCE is the primary phase in the drug development process. After completing the synthesis, the companies have two possibilities: They can either move into clinical trials on their own or license the new chemical entity to any other company.
When the companies opt to license NCE to another organisation, the expensive and lengthy clinical trials process is avoided. This is because the licensee company would conduct the clinical trials and manage the subsequent launch of the drug.
Many companies are implementing this business model to generate a higher margin level, and the companies can get a substantial one-time payment for the NCE. Moreover, the companies also enter into a revenue-sharing deal with the licensee company.
NCEs are chemical molecules and ultimately, after successful clinical trials can emerge as critical components in drugs. However, despite their urgency in the treatment of any indication, almost one-third of drug molecules do not succeed in the pre-clinical developments, which can often be attributed to compromised NCEs.
What are the main challenges in NCE development?
The key reasons many companies face challenges during the development of NCEs is uncertainty. No one can be sure about an NCE molecule activity like how it reacts under various situations, including how much time it could take to achieve the desired result or what challenges could evolve in raw materials.
Here are a few challenges that many developers face during the manufacturing-
Sourcing the highest quality raw materials- The concerns related to the quality of raw material for NCE are critical for Contract Development and Manufacturing Organizations (CDMOs). However, even with the highly diligent sourcing as well as the strongest supplier alliances, several factors might go wrong.
They can fail to meet the requirements which are outlined in the DME (Drug Master File). CDMOs should make sure that they are receiving superior quality raw materials.
Issues related to yield- Organic compounds are certainly not in the pure form. When they are isolated from natural sources or produced through organic reactions, they always comprise some other compounds. Before conducting the quantitative and qualitative assessment of organic compounds required to characterise them, it is necessary to purify the compounds.
Moreover, purification is a significant step in manufacturing the drug, assisting the elimination of unwanted materials that can compromise the efficacy of the drug or can be hazardous.
Scale-up Difficulties- For the manufacturing of an NCE and increasing production in any manufacturing plant can lead to very different outcomes. When bringing a molecule to the suites of cGMP for the first time, the process can take longer time, as per the requirement of greater supervision as well as quality control.
It is often challenging to simulate the suite of cGMP in the laboratories. Therefore, new impurities show up or an issue can be seen in the crystallisation of materials.
Some specialists suggest that further screening attempts in early development can smooth the pathway during the late stages of the development for reducing risks during late-phase.
Analytical Issues- A manufacturer of NCE qualifies an analytical method for assessing that the compound is suitable for the intended purpose. For this purpose, it is advisable to compare some specific samples of the compound to a standard one for testing the reproducibility.
Many companies perform this method during pre-clinical stages for determination of the feasibility for the NCE.
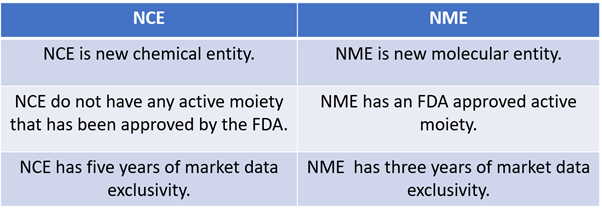
What is the difference between an NCE and an NME?
The main difference between NCE and NME is that NCE does not have any FDA authorised active ingredient, although NME has an FDA approved active moiety which has not been previously approved.
The terms NCE and NME are used for drug categorisation based on whether active moieties are present or not. Active moieties are the portions of drugs that can affect its activity against any indications.
Furthermore, there is one other difference between an NCE, and an NME related to market data exclusivity period. For NCE, the exclusivity period is five years, while it is three years for NME.
What is the market exclusivity for NCE?
The FDA grants exclusivity to an NCE. This exclusivity offers the license holder of an approved new drug application (NDA) limited protection from further competition in the marketplace for the innovation represented by its approved drug product.
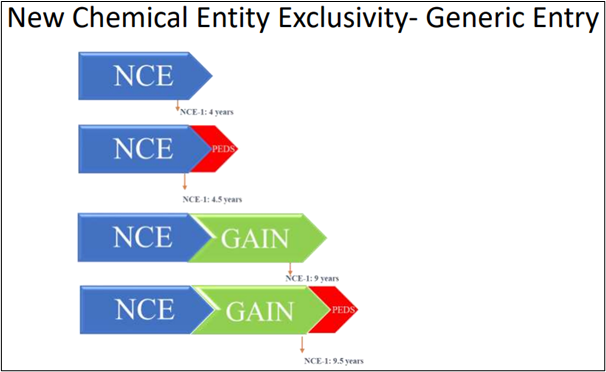
Source: FDA Website
 Please wait processing your request...
Please wait processing your request...