What is a New Drug Application?
A New Drug Application (NDA) of the US FDA (Food and Drug Administration) is an application by which drug developers or sponsors formally seek the FDA approval for a new drug for sale and commercialization in the United States.
A New Drug Application (NDA) informs the complete information of a new drug molecule. The purpose of NDA is to prove that a drug is safe & effective for its expected use in the large population study.
According to the FDA, 30% or less of initial drug candidates proceed through the complete multi-year drug development process, concluding with an NDA approval, after successful completion of the clinical studies and then the review of the clinical data.
New Drug Applications are usually regulated by the Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) of the FDA.
The filing of an NDA, after successful completion of clinical trials, represents a crucial breakthrough for a new drug. An NDA filing is a critical milestone for any organization, and investors keep a close watch on the process. The fate of any pharmaceutical company can change when the FDA passes an NDA approval of a new drug. This step is more crucial for small-cap healthcare companies, as their market value can change once their drug candidate receives approval.
After the submission of the NDA, the probability of a drug getting approved is very high. Accordingly, healthcare companies that file NDA witness a rise in their share prices even before the response from the FDA.
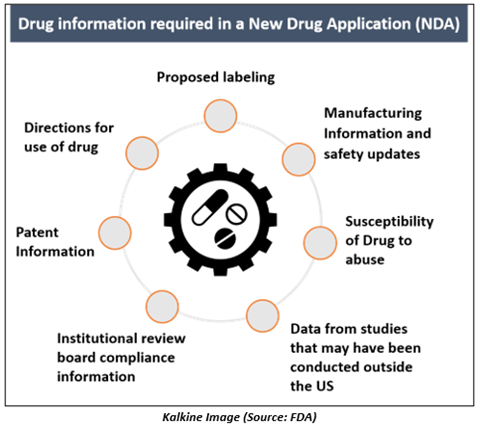
What is included in a New Drug Application?
The objectives of the NDA are to provide adequate information to permit FDA reviewers to determine the comprehensive history of the new drug candidate. Some facts that are required for the new drug application are-
- Information related to patent, manufacturing, and safety of the drug.
- Specific effectiveness for the proposed use(s) of the drug when used as directed.
- Reports on the design, compliance, and conclusions after completion of clinical trials by the Institutional Review Board.
- Susceptibility of the drug to abuse.
- Proposed labeling and directions for drug use.
An NDA comprises sufficient information for the FDA to determine the safety & efficacy of a new drug. The information should justify whether the benefits of the drug outweigh its risks, the proposed drug label (package insert) is appropriate or not, and whether manufacturing standards are adequate.
The information included in a New Drug Application is based on laboratory, preclinical testing on animals as well as human clinical trials.
Once an NDA is filed, the Food and Drug Administration reviews the product label (package insert) to be confident that the clinical information needed to use this drug safely is outlined. The agency also takes action to examine the manufacturing facilities where the drug will be manufactured.
What are the resources required for an NDA Submission?
The documentation needed for an NDA is intended to describe the complete information related to the drug. This information also includes what happened during the clinical trials, ingredients of the drug, results of the animal trials, pharmacodynamics, and manufacturing, & packaging of the drug.
The subsequent resources provide summaries on NDA content, format, and classification, including the NDA review process-
- Guidance Documents for NDAs- Guidance documents for the new drug application represent the current thinking of the agency on a particular subject. Guidance documents are made for FDA review staff as well as sponsors to give guidelines to the content, processing, and evaluation of applications. These documents also help to design, manufacture, and test regulated products.
- Prescription Drug User Fee Act (PDUFA)- Some pharmaceutical companies pay for an expedited review with the FDA through a procedure known as Prescription Drug User Fee Act (PDUFA), that is enacted in 1992. This Act permits the FDA to access more resources to fast-track the process of approval. Several essential drugs have been approved through the Prescription Drug User Fee Act, including treatments for cancer, heart disease and AIDS.
- Advisory Committees- Advisory committees offer independent advice along with recommendations to the FDA on scientific & technical matters related to the development as well as evaluation of products regulated by the agency. Though advisory committees only provide suggestions to the agency, final decisions are made by the FDA.
- Laws, Regulations, Policies and Procedures.
- NDA Forms and Electronic Submissions.
Final Drug Approval
After the final approval, the drug becomes accessible for prescription by doctors. However, drugs might not come to the market with immediate effect because of patents disagreements, manufacturing issues, or controlled substance designation from the DEA.
Usually, the pricing is revealed after approval. However, the FDA generally does not consider the pricing of drug or any economics as part of the approval process. In contrast, many other nations consider the economic effects of new drugs in their society.
 Please wait processing your request...
Please wait processing your request...