What do you mean by onshore?

Source: © Ribeiroantonio | Megapixl.com
While dealing with hydrocarbon exploration or production, the term onshore refers to the location of an operation on land. All the activities like exploration, drilling, production, installation of the rig, and transportation of produced hydrocarbon are done through the land rather than an offshore water body. Basically, onshore refers to all operations and processes related to extracting hydrocarbons from the subsurface to the surface that take place from the land.
How is onshore drilling different from offshore drilling?
Based on drilling oil, it can be classified under two main subclasses: onshore drilling and offshore drilling. Let us discuss them briefly to understand the basic difference between them.
Onshore drilling is the process of drilling an oil well deep into the Earth's subsurface from a land-based drilling platform. On the flip side, offshore drilling involves drilling a well originating from the sea bed.
The world's most hydrocarbon production comes from onshore drilling. The equipment used in onshore drilling is relatively simple and cheap compared to offshore drilling. Offshore drilling is a delicate job. Every single step in offshore drilling is performed with delicacy and experience.
The transportation of equipment and setting up a platform in an onshore operation is relatively easier than that of an offshore operation. The transportation of crew and its safety is much more expensive in offshore drilling compared to onshore drilling. The operating cost of land-based drilling is much lower than that of offshore rigs.
How are hydrocarbons formed?
Based on the most widely accepted theory of the origin of oil and gas, hydrocarbons are formed by the dead and decay of plants and animals under the influence of temperature and pressure. Various research results indicate that the zooplanktons form petroleum and natural gas. As per the theory, these zooplankton and algae die and get settled on the ocean floors. Over time, the deposited zooplankton and algae are deposited by various layers of sediments. With sedimentation, the deposited layers subside and undergo pressure and temperature change.
As the deposition process continues, the accumulation becomes denser. At increased temperature and pressure, the organic matter starts decaying and converts into kerogen. This process is known as Catagenesis. Organic matter is cooked under high temperature and long-chain kerogen molecules are broken into smaller chain hydrocarbons during the catagenesis. This process may take millions of years. The temperature decides the cracking of long-chain kerogen into small chain hydrocarbons. If the temperature remains higher, thermogenic cracking occurs, and gas molecules are formed, whereas, at relatively lower temperatures, other than the oil window temperature, the catagenesis process can't proceed.
Where are the world's most hydrocarbons deposited?
The world's most hydrocarbon is deposited in the Middle East. Since petroleum is the main source of the world's energy supply, every nation across the globe is hunting its deposited hydrocarbon resources.
Scientists believe that the current region of the Middle East that is mostly a desert in the present time, was not always the same earlier. They believe that the area was a massive water body named Tethys Ocean, which fed nutrients into the ocean. But the land in modern time rose due to the tectonic activity, and Tethys ocean receded. Sandy and dry Middle Eastern desert remained in place. However, huge deposits of hydrocarbon are also buried under the ground, making the region the hottest and biggest province for oil and gas deposits.
Summary
- All operations and processes related to extracting hydrocarbons from the subsurface to the surface that take place from the land are known as onshore.
- Onshore drilling is a process of drilling an oil well deep into the Earth’s subsurface from a land-based drilling platform whereas, offshore drilling involves the process of drilling a well originating from the sea bed.
- The Middle East is the world's largest oil province of the world that was previously drowned under the Tethys Ocean.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
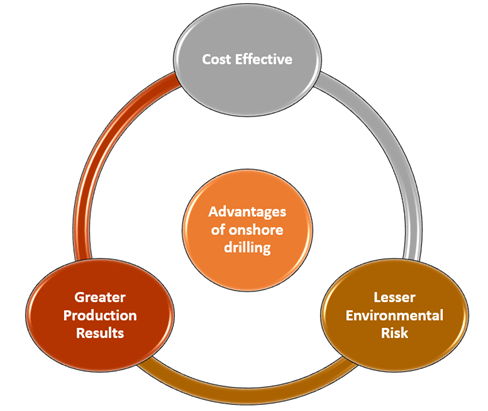
What are the advantages of onshore drilling?
There are numerous advantages of an onshore oil and gas drilling process. Let us discuss them one by one briefly.
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
- Cost-Effective: The installation and set up of an offshore drilling platform requires a lot of time. The daily cost incurred in this process piles up till the production from the well starts. The cost of offshore equipment along with the crew's transportation cost and living cost also add up and make the offshore drilling process more expensive than an onshore drilling process.
- Lesser Environmental Risk: Onshore drilling offers a lower environmental risk compared to an offshore operation. We have seen the disruptions and environmental effects caused by most of the oil spills which took place in oil and gas history. It doesn't mean that onshore operations are risk-free, hydraulic fracturing and onshore rig installation also creates a lot of environmental issues but compared to offshore the impacts are relatively less.
- Greater Production Results: There are more plentiful resources located under the land. Currently, more than 70 per cent of the world's total hydrocarbons come from the drilling of an onshore oil and gas well, and the remaining 30 per cent is limited to offshore production.
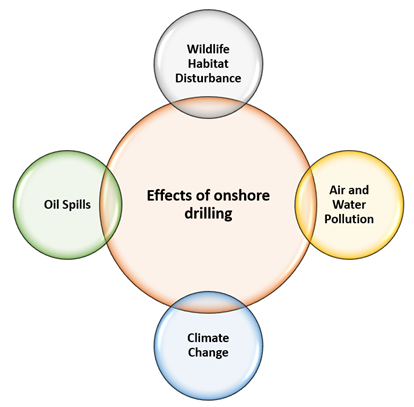
How onshore drilling affects the environment?
There are various ways by which onshore drilling affects the environment. Let us try to glance at the few most prominent environmental impacts.
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
- Wildlife Habitat: Onshore oil and gas drilling disturbs the natural ecosystem by disturbing the natural habitat for wildlife.
- Air and Water Pollution: The onshore drilling process can potentially affect the area's local air and water quality.
- Climate Change: The release of greenhouse gases released from the exploration and production of oil and gas releases greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere, which is a potential cause of global temperature rise.
- Oil Spills: Oils spills are not limited to offshore only. Onshore oil spills degrade the soil quality, disturbs wildlife habitat and natural vegetation of the area.
 Please wait processing your request...
Please wait processing your request...