Original Equipment Manufacturer produces goods and services that are used by other companies to manufacture or use finished goods. Original equipment is an essential component of finished products for many companies.
Over time, the OEM industry has evolved that built products destined for rebranding and reselling by other companies, which were the clients of OEMs. Now the scope of industry covers a wide range of producers, including software developers in the IT industry.
A prime example of software OEM could be Microsoft, which develops windows operating system used by a majority of personal computer/laptop manufacturing names like Dell, Lenovo, HP, Asus, Samsung etc.
As technology and software continues to penetrate in broader industries to improve operating efficiencies and enterprise management, the significance of software OEMs has also grown in the corporate ecosystem.
Why are OEMs important?
Manufacturing a product or developing software requires companies to invest in capabilities and make the best out of those capabilities. Companies may choose to do so, but it requires a greater level of investments, which comes with associated risk.
Now OEMs come into the play, having developed capabilities and capacities over time, by manufacturing goods and developing service offerings. In a market where companies dedicate quality time on marketing, customer engagement, and market penetration, OEMs execute manufacturing of goods and services.
With such offering by OEMs, the clients of OEMs are able to emphasise on other crucial aspects of business like branding, marketing, customer experience, proprietary design, and research and development.
An example of this could be Apple Inc., which does not manufacture the components of its flagship products and outsources functions to other companies like Foxconn, Wistron, Pegatron, Luxshare, Goertek, Qualcomm, Intel, Samsung etc.
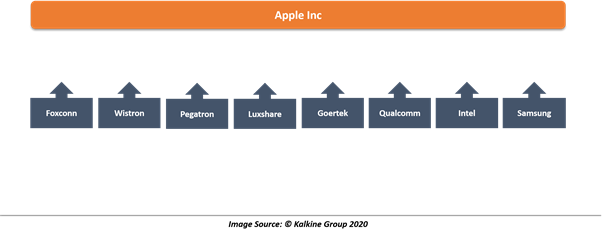
OEMs essentially operate as a supplier to many industries and undertake the crucial development of original equipment to be used in the finished product, which will be eventually sold by other company after assembling and branding.
Firms that outsource business to OEMs are benefitted by reducing the direct costs of the business, which are fixed in most cases. They emphasise on design and product life cycle, which could be shorter, given that breakeven is not necessary without manufacturing.
In this way, the clients of OEMs focus on their core competency such as research and development, design, customer satisfaction, marketing, customer engagement etc. OEMs are limited to manufacturing and rarely commercialise their products to retail clients.
What are the hardware OEMs?
In the hardware business or core manufacturing, OEM companies serve a wide range of clients which sell goods like television, mobile phones, personal computers, automobiles, printers etc.
Hardware OEMs manufacture items like processors, motherboards, hard drives, engine components, television components, mobile phone components, etc. They design, engineer and manufacture complete products, and some also manufacture components.
The other type of manufacturers is Original Device Manufacturers (ODMs), which design and manufacture finished products. The products made by ODMs are usually branded by other companies and sold to end-users.
What are software OEMs?
In the software category, the players are evolving rapidly and include several well-established companies like Microsoft, Oracle, SAP etc. While Dell, Asus or Samsung may assemble a personal computer or laptop, the software used in these is largely supplied by other companies.
A product comes with software applications with it. Such as cars now have embedded user interface, mobile phones use operating systems, computers require operating systems, large machines have operating software, mining companies use mining-related software.
As economies continue to embrace technology and digital future, the significance of software OEMs continues to grow. A wealth management platform used by wealth managers would also count in software OEMs.
Similarly, there are software companies that sell platforms for human resource management, market data, etc. Software OEMs are mostly embedded in the finished products used by customers at large.
Why companies prefer outsourcing to OEMs?
Cost reduction
When companies are outsourcing manufacturing of products and components, they do not invest in manufacturing facilities and capability development. It saves a lot of costs for the companies and allows to focus on core competencies.
With cost reduction, it allows companies to invest in other areas such as branding, marketing, research and development, customer engagement. Outsourcing also alleviates the risks associated with the manufacturing of components or products.
Quality and specialisation
Original Equipment Manufacturers have developed capabilities and capacities over time. A precision component expert knows in and out of the manufacturing processes, quality control and delivery. Given their expertise in manufacturing, the response timing and service is quite competitive and efficient.
The investment in capacity and capability by OEMs allows maintaining the quality of the products, which is also driven by experience in manufacturing and handling customised requests of the clients. OEMs try their best to match the expectations of clients.
Customer service and after-sale offerings
A great OEM company thrives on its customer servicing capabilities. The partner company has expectations from the supplier, which is taken as a benchmark for the services offered by the supplier/OEM. Since there is intense competition between low-cost OEMs, they intend to deliver above-par customer service to maintain their name in the industry.
The companies that outsource manufacturing to OEMs also get after-sale services like a warranty on the products sold. The partner company, therefore, gets further value by the services offered by OEMs.
Economies of scale and labour costs
Large OEMs also leverage economies of scale to improve the cost base of the products, thus offering products with competitive pricing. With large scale production and investments technology, it allows OEMs to lower their costs.
Manufacturing has been a major driver of development in the Asian region, which has relatively lower labour costs compared to developed economies. As a result of low labour costs, OEMs provides significant value to customers in terms of pricing and costs.
Supply chain diversification
With a host of OEMs across regions, the companies that outsource manufacturing to OEMs take the benefit of supply chain diversification. Given the globalisation and interlinked supply chains, a single source of manufacturing would mean higher supply chain risk for the company.
Companies may choose to pick different OEMs in different regions to complement the demand for the region or even export from the same region to other regions or markets. With several OEMs, the supply chain risk is also reduced via diversification.
 Please wait processing your request...
Please wait processing your request...