What is Proof of Work (PoW)?
Proof-of-work (PoW) is a consensus mechanism often adopted on a cryptocurrency blockchain. It is a tool to agree on account balances, order of transactions, etc. It is used to achieve decentralised decision making on a blockchain network. PoW requires nodes on a blockchain network to prove the amount of computational power to reach consensus. PoW thus helps prevent attackers or hackers from exercising control on the network. It also contains any insider influence on the crypto platform.
Highlights
- Proof of work is a blockchain or cryptocurrency network consensus mechanism.
- It requires nodes on a network to provide evidence that they worked or used computational power.
- Proof-of-work works to protect the blockchain from any outside attacks.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How does the PoW system work?
PoW system requires nodes on a network to provide evidence that they worked or used computational power to achieve consensus on the network. Take, for example, the case of Bitcoins, where nodes tend to repeatedly hash algorithms. Whoever wins the round of hashing moves to the next block of transactions. The proportion of work done becomes the deciding factor here. Proof-of-work is the basis of determining the difficulty and rules of crypto miners’ work which is mining. PoW thus helps add valid blocks to the blockchain. More work done by nodes, the longer is the chain of hashtags and the higher the block number.
Once a hash is generated, it becomes easy for other miners and clients to verify transactions. Even if one transaction changes, the hash would be different, indicating fraud. Hashing under proof-of-work is, therefore, a big deterrent to attacks on the blockchain.
Image showing cryptocurrency blockchain technology concept
Image Source: © Al4k14 | Megapixl.com
Why is PoW needed?
- Cryptocurrency blockchains work on a peer-to-peer network by design and avoid centralised decision making.
- Therefore, decisions are based on a consensus. To achieve this consensus, the proof of work method is required.
- Other consensus mechanisms like proof of stake (PoS) and proof of burn can also opt on the network.
- Without a consensus method, the cryptocurrency network and all its data become vulnerable to hacking and theft.
- Other than being a consensus mechanism PoW also incentivises miners and also promotes new currency issues.
- Miners often get rewarded with crypto coins based on PoW. In Blockchain, the PoW algorithm is used to confirm transactions and produce new blocks; miners can also compete against each other and get rewarded.
- PoW also provides finality to transactions which are very important for decentralised applications (DApps).
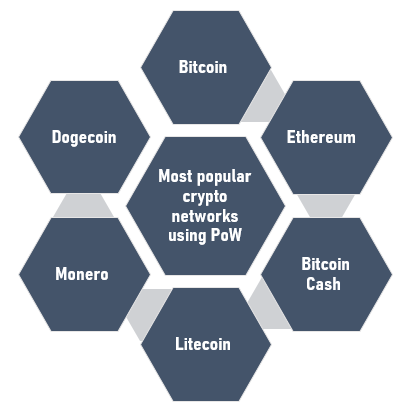
Which cryptocurrencies use PoW?
The PoW mechanism is visibly used in a lot of cryptocurrencies; the most well-known is Bitcoin. Bitcoin was the first cryptocurrency working under PoW type of consensus. Another well-known network is Ethereum. A lot of projects on the Ethereum platform, use the PoW consensus model. It is used for mining and token validation.
Source: © 2021 Kalkine Media
The mechanism used may be in the form of computational puzzles, hash sequences, etc. The idea is basically to give the users a challenge that gives them the accruing benefits when solved.
What are the pros and cons of PoW?
The PoW mechanism has the following benefits-
- It is a neutral mechanism and does not need a balancing mechanism.
- The two most popular crypto networks use it; Bitcoin and Ethereum, thus is a well-tested method.
- It helps keep transactions secure and the network decentralised.
- It is easier to implement when compared to the PoS method.
- As PoW requires high computation infrastructure, it has led to the development of mining pools.
- PoW also imposes limits on actions on the blockchain, protecting it from attacks.
- It helps with forming new blocks on the blockchain.
However, there are certain flaws to PoW -
- It requires a miner to spend a lot for improved computational possibilities.
- Highly specialised hardware may be needed for solving complicated PoW algorithms.
- As costs are high, mining pools are formed, which lead to lower levels of centralisation.
- Hardware used for PoW consume lots of power, making it energy inefficient.
- It also does not guarantee the security of the network.
- It is a very time-consuming mechanism of consensus development.
What are the alternatives of PoW?

Image showing crypto blockchain mechanism
Source: © Lembergvector | Megapixl.com
Here are the most used alternatives to the PoW method-
- Proof of burn-Here, instead of bringing the money together into computer equipment, the owner burns the coins. He thus gets a privilege to mine on the system. Burning works on random selection. However, it wastes a lot of resources.
- Proof of stake- Here, the coins exist from the start, and the validators get a reward in the form of transaction fees.
- Proof of capacity- Here, the algorithm generates plots or large data sets. These are stored on the hard drive; more plots on the hard drive improve the chances of moving to the next block. This method is again resourced intensive and may be costly.
- Proof of elapsed time- It is like PoW but more energy efficient. It does not involve any computational puzzles; it instead uses a trusted execution environment. It, however, leads to the involvement of a third party in the network, which is not considered good.
 Please wait processing your request...
Please wait processing your request...