Quarterly report
What is quarterly report?
A quarterly report is a compilation of unaudited financial statements released by companies every year, such as cash flow statements, income statements, and balance sheets. These statements can also include comparative results and year-to-date results in addition to quarterly results.
Highlights
- A quarterly report is a compilation of financial statements providing details about a company's results that is intended for shareholders.
- The executive summary, future strategy, highlights, and objectives are usually included in quarterly reports.
- Quarterly reports provide information to analysts and investors to help them determine a company's performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of a quarterly report?

Source: © Stokdrozdirina | Megapixl.com
Quarterly reports are unaudited financial reports that are summarised copies of financial statements issued by public entities every three months to comply with regulatory requirements.
These reports assist in the elimination of information asymmetry as well as the likelihood of any possible window dressing.
Gross sales, financial data, operational expenses, net profit, and cash flow are all included in quarterly reports. It is often followed by presentations from a company's management, including question and answer sessions and the presentation of key performance indicator data to investors and analysts. Firm management also offers guidance for potential financial performance.
Executive summary, highlights, priorities, and ongoing challenges are all included in a quarterly report. In terms of challenges, the quarterly report could include measures that have been prepared or implemented to address them. In addition, if appropriate, the quarterly report will evaluate data from previous quarterly reports and compare it to the current report.
Collecting financial and performance data from multiple sources ensures that the quarterly report is as accurate as possible; however, this takes time and involves extensive research; graphs and spreadsheets visually represent the data provided. Most significantly, quarterly reports assist analysts and investors in determining a company's health by presenting the information.
What does a quarterly report include?
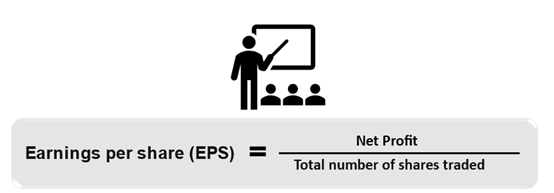
Earnings per share (EPS)
An investor must keep track of how the EPS is progressing. A higher EPS means that the business is doing well, resulting in higher profits for the shareholders.
Net profit is divided by the total number of outstanding shares to calculate EPS.
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
Gross sales
This is the company's "top-line," or turnover, which measures gross profit, sales, or earnings. A steady increase in the top line is a sign of rising demand and a healthy market. To determine the health of a company, gross sales must be considered over a period.
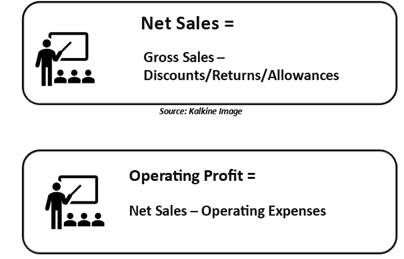
Net sales
This is a better indicator of real business health than gross sales. However, all specifics of sales discounts, refunds, and allowances granted are needed to measure the same.
Net Sales = Gross Sales – Discounts/Returns/Allowances
Interest rate
Interest is the sum of money charged for loans while running a company. As a result, a rise in the interest rate means an increase in the company's debt. If a rise does not follow the increased debt in revenue and earnings, the investors' profit margins would be reduced.
Operating Income
The corporation includes both operating and non-operating profits. Operating income is the measurement of the profit earned after deducting wages, depreciation of products, and other fixed costs.
Non-operating income, on the other hand, is income from sources other than the company, such as dividends, rental income, interest, and so on.
Operating Profit
Operating Profit = Net Sales – Operating Expenses
The cost of running a company is referred to as operating expenses like pay-scales, electricity bill, rent bill, expenses for the office and stationery, license fees, research and development costs, charges for legal and banking services. To arrive at the business's operating profit, other fixed and variable costs that are part of the operating expenses must be deducted from net profits. This figure is called the EBITDA (Earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization).
The operating profitability reflects current market conditions as well as management performance. The business would be better if the operating profit was higher.
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
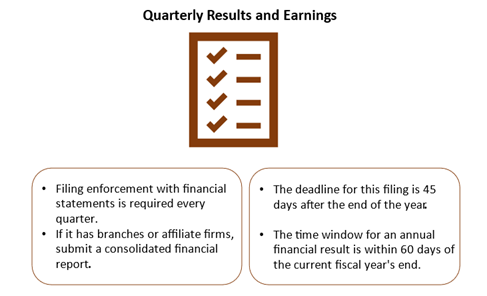
When should a company announce quarterly reports?
Every quarter in a year, publicly traded companies should report their results and earnings.
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
What are the differences between an annual report and a quarterly report?
The company is required to provide annual reports to its shareholders on a yearly basis. The quarterly reports are published every three months.
Management discussion analysis, auditor opinion, and financial statements for the current financial year will be included in the annual reports. The quarterly reports contain only unaudited financial statements and quarter financials from the previous year, with no auditor opinion or management discussion analysis.
Annual reports must be filed within 60 days, while interim financials must be submitted within 45 days.
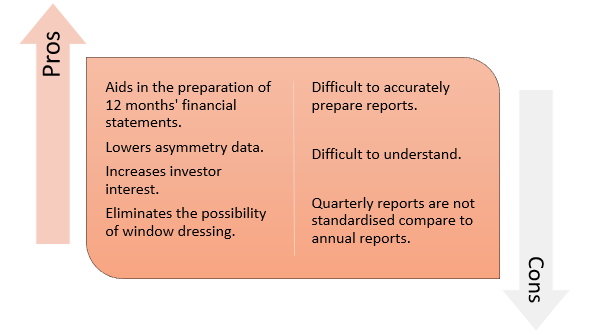
What are the benefits of submitting a quarterly report?
- It aids in the preparation of 12 months' financial statements, which are calculated by using two equivalent quarterly statements and one latest annual financial statement.
- It lowers asymmetry data.
- It increases investor interest, resulting in more capital being invested in the business.
- In terms of finances, it eliminates the possibility of window dressing, which is the practice of making year-end financial statements appealing to draw new investors to the business, resulting in the presentation of clear financial statements.
What are some of the drawbacks of quarterly reports?
- It is difficult to prepare these reports accurately.
- Since these reports are not audited, they can be difficult to comprehend.
- Any details contained in quarterly reports but not in annual reports may affect the business's growth prospects.
- When opposed to annual reports, in most cases, these reports are not standardised.
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
 Please wait processing your request...
Please wait processing your request...