What is recurring revenue?
Recurring revenue is a type of sales income that is generated repeatedly over a considered period. It is the revenue generated when customers purchase a service consistently, giving the service provider the ability to project future revenue streams. A business can calculate recurring revenue with metrics like user growth rate, average revenue per user, subscriber rate, etc. The ARR (annual recurring revenue) and MRR (monthly recurring revenue) are computed using these metrics. It is the underlying sales mechanism for any subscription-based company. It helps compute a realistic and accurate amount of future income. The predictability from such kind of revenue attracts investors towards a recurring revenue business model.
Summary
- Recurring revenue is a sales model. It quantifies the amount of revenue a company can generate repeatedly.
- Service sector firms commonly use revenue models, like software companies, media apps, etc.
- It is a very predictable and growth-oriented revenue model.

Source: © Dizain777 | Megapixl.com
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)-
What are the popular types of recurring revenue models?
Recurring revenue models can be encountered in various forms, like-.
- Hard Contracts- where customers sign a contract covering a period in which they make monthly payments.
- Auto-renewal plansare automated versions of recurring revenue collected from a customer until they cancel the subscription. They are sometimes called evergreen plans.
- Subscriptions- are for a finite period having an option for continuity. Typical examples are Netflix or Spotify.
- Tiered bill- another way of breaking down the entire bill into small streams of recurring amounts during a term. It is commonly found in contracts signed by architects or engineers.
- Usage-based subscriptions- billing based on service usage but at regular intervals. Any utility bill like electricity and water are an example of it.
How is recurring revenue different from non-recurring revenue?
Both revenue models are different. The prominent variations are shown below-
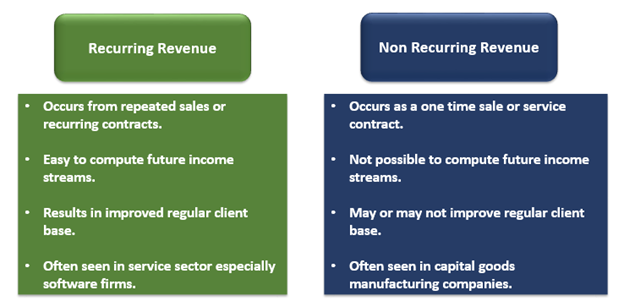
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
Examples of recurring revenue are-
- Software services provided to clients.
- Subscription paid to an online streaming app.
- Web-based subscription magazines.
- Paid web hosting platforms.
- Subscription-based applications on phones.
Examples of non-recurring revenue are-
- A one-time sale is of a capital good.
- Single term contracts for road construction.
- Retail goods sold on customer needs which are not regular.
What is ARR? How is ARR computed?
ARR or annual recurring revenue is the revenue collected on an annual basis. Payment for services provided is received from customers at the end or beginning of a year. Often a KPI in the software industry helps quantify a company’s progress and forecast its revenue. ARR can be further broken down to track growth in various customer segments helping in revenue generation.
The calculation of ARR is straightforward. Suppose a customer JH takes up a five-year plan for a streaming app for a total amount of AU$200,000. He decides to make annual payments. The ARR can be determined by dividing the total plan amount by the time the contract has been signed. It means-
ARR = AU$200,000 / 5 = AU$40,000
It simply means that the company will receive AU$40,000 from JH annually for the coming five years.
Companies often break down ARR based on the customer segments like new, old, premium, etc. Such a breakdown helps in identifying the best contributing segment to overall revenues.
What are the other common terms related to recurring revenue?
- MRR or Monthly recurring revenuemeasures the total predictable revenue a firm can receive every month. It is often used for financial forecasting or to track growth and sales momentum.
- ARPU or Average revenue per user- is the average revenue each user contributes. It is computed by dividing annual or monthly recurring revenue by the average number of users.
- LTV or Lifetime value- It is the total amount to be received by a firm from a single customer throughout their term of using the firm’s product/ service. Rising LTV is a sign of the growth of the business, while a declining one shows lower revenue acquisition.

Image Source: © Anatoliishcherbatiuk | Megapixl.com
What is the use of recurring revenue?
- Recurring revenue is essential for understanding the growth and profitability of operations. Tracking recurring revenue regularly helps in determining.
- It helps identify high-value customers who spend the most on a company’s product/ service. It is also valuable for identifying the high-value segments of business or geographies generating maximum sales.
- Recurring revenue tracking is helpful to identify close-to-churn customers who have shown lower usage rates in the recent past. Such customers are then offered discounts, or feedback is obtained. These are tricks for customer retention.
- Predictability is enhanced using this metric. ARR, MRR is therefore used by companies to forecast future revenues. It is even helpful for business valuation and sales projection.
- Recurring revenue as a metric quantifies a company’s growth. It is measured in various ways and has numerous utilities within a business adopting such a revenue model. In addition, the quantity obtained is often used as a KPI for decision making and strategy formulation.
- It helps evaluate the success of a business model. For example, a growing recurring revenue talks a lot about customer retention, satisfaction, and relation. A company can get to know whether its subscription model is successful or not.
 Please wait processing your request...
Please wait processing your request...