What is short selling?
Short selling refers to the sale of a stock which an investor does not own. When an investor short sells, he sells a stock that he is not in his possession. He borrows the stock and sells it in the market and then later covers it by buying it from the market. This type of strategy is used mostly by speculators and can also be used by hedgers.
Investors short sell when they expect the prices of the stock to decline in the future. Such price movement is the expectation against which the investors believe they would be able to buy the stocks in future and gain a profit too.
The term “short selling” differs from the terms “going short” or “shorting”. Going short on a stock simply means selling that stock, while short-selling means selling a borrowed stock. Therefore, both terms are to be used carefully. Alternatively, “going long” means buying an instrument.
How is short selling done?
While short selling a stock, an investor borrows stock from an existing owner, that is usually a Broker. This transaction takes place with a future promise of replacing these stocks. The investor would then have to buy back these stocks from the market and then would have to return them to the broker.
This is exactly why the expectation of a future decrease in prices is important. The complexity of the entire procedure makes it risky in nature.
The lender may force the investor to return the stock within a limited time frame. Investors cannot sell what they do not own, this means that the stocks lent to an investor belong to the broker’s inventory or belong to another brokerage firm.
If the prices of the stock were to go up, contradictory to the expectations of the investor, then he would incur a loss. In either case, the investor must return the stocks to the broker even if that means buying them from the market at a higher rate.
The broker may also charge a lending fee from the investor. It is important to note that the stock lent by a broker is owned by him and not the investor. Thus, the dividend from the stock should be given to the owner of the stock. Therefore, when an investor returns the borrowed stock, he must pay the fee along with any dividends received by him.
The investor must also pledge a security against the borrowed stock from the broker. This aspect makes these stock loans secured because there is collateral that is offered against them.
The borrowed loans can be of two types: Call Loans and Term Loans. Call loans can be terminated anytime depending on the lender, while term loans are provided for a specific period.
What are the advantages of short selling?
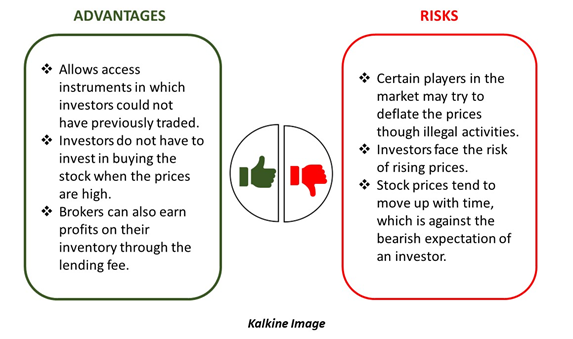
Short selling allows access to those instruments to the investors in which they could not have previously traded. They can achieve this with the help of borrowed instruments. Also, investors do not have to invest in buying the stock when the prices are high; indeed, they have an opportunity to buy the stock when it’s at a lesser price in the near future.
Moreover, the broker can also earn profits on his inventory through the lending fee. Broker may also increase the fees during excessive short selling of a stock or an instrument in the market. Thus, it is possible to earn profits on stocks lying passively with a broker.
Short selling may allow investors as well as brokers to earn a profit even when the market is going down.
What are the risks associated with short selling?
Certain players in the market may try to misuse short selling of instruments. They may also use illegal methods to deflate the prices of the stocks. Because of this reason, the risk associated with short selling is high as there is increased volatility in the market.
The investors face the risk of rising prices as well. If the prices go on increasing indefinitely in the market, the investor’s risk would also increase proportionately to that rise. Thus, practically, the investor does not have an upper bound to the amount of loss he might face if the prices go on increasing.
Stock prices tend to move up with time. However, an investor has bearish expectations when he goes for a short sell. Therefore, the upward trend of the stock market might challenge the expectations of decreasing prices that an investor had. Also, the timing of the investor is crucial. As an investor waits to book higher profits in future, he may end up incurring losses.
For these reasons, short selling should only be done by experienced investors. This holds true especially for investors who want to speculate rather than a hedge. Speculating with a short selling strategy can prove to be very risky and can lead to huge losses due to market volatility.
Why do investors opt for short selling?
There are two main reasons for short selling an instrument:
- Speculating: As discussed before, an investor who sees an opportunity of profiting from falling prices can short sell a stock he does not own. Thus, investors who enter the market with the intent of only profit making are called speculators.
- Hedging: Hedging refers to securing one’s position against risk. Most active short sellers are the ones who want to secure another long position by an offsetting short position.
What restrictions are imposed on short selling?
Not every type of financial instrument is available for short selling. There are guidelines regulating short selling. Many markets do not allow investors to short sell in order to curb illegal activity that leads to lowering of market prices.
There is also the requirement of a margin to short sell. This margin may be high or low, depending on the type of securities. Thus, the short selling market is not for inexperienced players. The costs associated with short selling may overweigh the revenue from it if the market conditions are not predicted rightly.
 Please wait processing your request...
Please wait processing your request...