What is spinoff?
A spinoff is a corporate operational strategy used to dissolve a subsidiary business from its parent based on operations. Under a spinoff, a parent company separates a part of its business operations by making another publicly traded entity. The important differentiating fact is that all existing shareholders of the parent become shareholders in the new entity. The entity formed pays the necessary consideration to the parent company for any assets, including brands and employees taken over. It may sometimes even absorb a debt of parent as consideration for assets taken over. It essentially reorganises the operational structure of a business to improve its profitability.
Highlights
- A corporate spin off is a strategic move often undertaken to obtain the benefits of specialised operations.
- Spinoffs also help in diversifying the business risks of a group.
- Investors may have an option to either hold shares of the parent or the spun-off entity.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
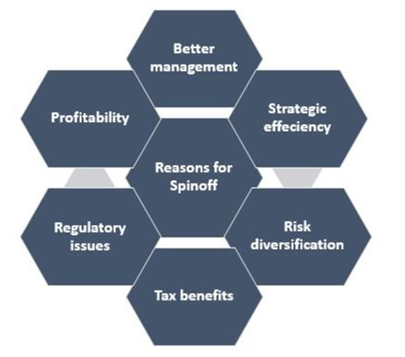
What are the reasons for spinoff?
A company may opt for a spinoff for the following reasons.

Source: © Innuasha84 | Megapixl.com
- It is difficult for a single set of people to manage a fully diversified business group.
- Spinning off various operational units into separate entities can strategically help enhance efficiency and effectiveness.
- As the economic environment changes, certain structural reforms are needed to remain profitable and continue business sustainably.
- Spinoffs help in diversifying the business risks of a group. The risk is spread over to different entities with the spinoff, not letting one subsidiary affect the other's performance.
- Separating out unregulated businesses from the regulated ones may be another reason for a corporate spinoff.
- Often companies go for a spinoff to enhance taxation benefits available in one business, which may not be claimable as a consolidated organisation.
- Sometimes spinoffs may become essential to create enhanced shareholder value in the capital market or create a movement in them, which otherwise may not be possible due to the stability achieved by a business.
Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
Thus, a corporate spinoff is often the parent entity's way to reduce agency costs, create tax benefits, or enter a new industry. A company may spin off a less productive division to work on its profitability independently.
What is the process of a spinoff?
The following steps are involved in a corporate spinoff process
- First, a spinoff announcement is made specifying the number of shares existing shareholders will receive.
- Next, it must get regulatory approvals for the same; it should also confirm the taxable status.
- Approval from shareholders is also needed before the spinoff.
- Next, a trading date can be set on a when-issued basis.
- After this, the corporate spinoff takes place, and shares of the new entity are ready to trade in the market.
- Information regarding financial statements and spun-off company's value must be made public.
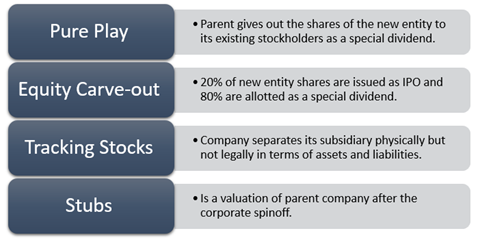
How many types of corporate spinoffs are there?
Based on ownership retention, we can classify spinoff as
No ownership spinoff- here parent company may choose not to retain any ownership in spunoff business and distribute ownership rights to its own existing shareholders. There is autonomy here in the new entity's operations.
Minority ownership spinoff- here, the parent may hold a maximum of up to 20% in the new entity. The remaining 80% is distributed among parent's shareholders on a pro-rata basis. In this way, the parent retains some control and decision influencing power in the spunoff company.
Other types of corporate spinoffs are-
Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
What are some pros and cons of corporate spinoffs?
Following are the benefits of corporate spinoffs-
- A company can achieve operational expertise through a corporate spin off to develop each business into an independent brand.
- The spun-off entity can improve its profitability exceptionally well over others as it will streamline its focus on its core business model.
- Due to enhanced profitability, a spun-off company can even attract new shareholders or institutional investors.
- As management separates out, a new leadership team of the spun-off entity is formed, allowing them to explore their leadership potential.
- Corporate spinning-off also serves investment objectives for the existing and/ or prospective investors who may see great potential in the separated business segment.

Source: © Convisum | Megapixl.com
Following are the disadvantages of corporate spinoffs-
- Spinoffs may prove to be costly for the parent company.
- It may cause employee discomfort and job changes or even job loss.
- There may arise certain revisions on contractual obligations, like loan agreements, vendor agreements, etc.
- A spin off doesn't take place in a day or two and may require a long-term commitment from the management.
What is the effect of spinoff on share prices?
Often after a spinoff, the share price of the parent company gets reduced. It is because existing shareholders becoming sceptical about the future of the company. Plus, they have also already received a stock dividend on the shares. Therefore, as a market reaction, the share price dips.
Furthermore, investors may have an option to either hold shares of the parent or the spun-off entity. Many of them might want to shift to the benefits of specialisation being offered by the new company. It is also possible that some investors may stick to the parent company based on its stability, strong market cap and low-risk returns.
It is observed that spunoff companies outperform in strong markets while underperforming at weaker times. Therefore, investors who have a better risk appetite tend to invest in them.
Also, if the parent company is a part of an index, it is stripped off the index after spin off due to a reduction in market capitalisation. This sometimes results in a lost reputation amongst retail investors.
 Please wait processing your request...
Please wait processing your request...