What is S&P/ NZX 50 index?
S&P/ NZX 50 is the benchmark stock market index of New Zealand. The value of 50 largest and most liquid stocks, listed on the main board of New Zealand Stock Exchange is tracked by the index based on their market capitalisation. The index covers about 90% of New Zealand’s equity market capitalisation.
The S&P/NZX 50 was launched on March 3, 2003 and is symbolized as NZX 50. It is widely considered the key gauge of New Zealand’s equity market and the most-quoted index in New Zealand.
Summary
- S&P/NZX 50 is the benchmark stock-market index of New Zealand that comprises 90% of the equity market capitalisation of New Zealand.
- The index is widely considered as the primary barometer of New Zealand’s equity market.
- Market capitalisation and liquidity obligations need to be fulfilled for a stock to be eligible for inclusion in the index.
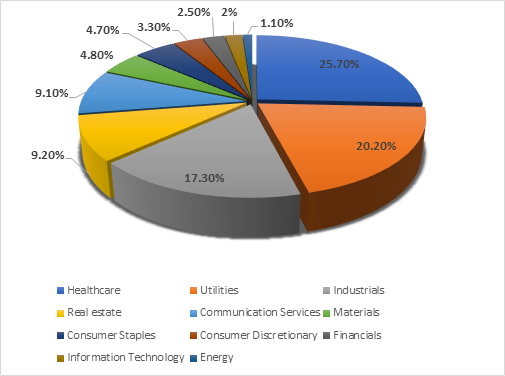
- Healthcare sector constitutes the most weight in the index followed by utilities and industrials.
- S&P/NZX 50 index is rebalanced quarterly in March, June and subsequently in September and December.
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
Why S&P/ NZX 50 was created?
The index was created to track how the largest index-eligible stocks listed on NZX Main Board (NZSX) by float-adjusted market capitalisation have been performing. The index comprises of 50 biggest companies.
Which companies are eligible for inclusion in the S&P/ NZX 50 index?
Dual and overseas listings are qualified to be included in the S&P/NZX 50 index. The index can include all common and equity preferred stocks that are not fixed income.
ALSO READ: What makes New Zealand stock market unique? How is NZX 50 performing?
Hybrid stocks, equity funds (closed and open-ended) that invest in a portfolio of shares and companies considering merger & acquisition are not eligible for index inclusion.
How are stocks selected for S&P/ NZX 50?
The NZX Main Board's set of ordinary equity stocks is used to create the index components.

Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
Market capitalisation is a key yardstick for choosing a stock in the S&P/NZX 50 index. Stocks are added in the index if they are sufficiently large to fulfil the minimum ranking conditions for the index.
The S&P/NZX 50 index also has liquidity obligations to make sure that only stocks that are often traded are added.
The below liquidity requirements must be met for a stock’s inclusion.
Relative Liquidity- For index inclusion, stocks must have a relative liquidity more than 50% of the market liquidity over 6 months of the evaluation period.
Absolute Liquidity- For index inclusion, stocks must have an absolute liquidity of more than 2.5% over the 6 months of the evaluation period.
What are the top 5 constituents of S&P/NZX 50 by index weight?
Below are the top 5 constituents of the S&P/NZX 50 by index weight.
1. Fisher & Paykel Healthcare Corporation Limited (NZX:FPH, ASX:FPH) (Healthcare sector)
2. Auckland International Airport Limited (NZX:AIA; ASX:AIA) (Industrials sector)
3. Spark New Zealand Limited (NZX:SPK; ASX:SPK) (Communication services sector)
4. Meridian Energy Limited (NZX:MEL, ASX:MEL) (Utilities sector)
5. Mainfreight Limited (NZX:MFT) (Industrials sector)
Who maintains the S&P/NZX 50 index?
The S&P/NZX Index Committee is in charge of maintaining the index. The Index Committee is made up of full-time employees from S&P Dow Jones Indices and the New Zealand Exchange. The Index Committee meets on a regular basis.
DO READ: What is NZX, and what are NZX50 companies?
At each meeting, the Index Committee may examine pending corporate operations that may have an impact on index constituents, information comparing the index's composition to the market, companies being selected for inclusion in the index, and any important market events.
How is the S&P/ NZX 50 index constructed?
The index is computed using a base-weighted aggregate algorithm. The index's level indicates the overall market value of all component stocks in comparison to a certain base period.
What are the characteristics of S&P/NZX 50 index?
The S&P/NZX 50 has 50 constituents with a mean total market capitalisation of 17,169.35 million as of May 31, 2021.
The top 10 constituents of the index make 59.1% of the index’s weight with the largest constituent weighting 13.6%.
Healthcare sector weighs the largest i.e. 25.7% of the index, followed by utilities (20.2%), industrial (17.3%) and real-estate (9.2%).
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
What information does S&P/ NZX provides?
The S&P/NZX family of indexes tracks the performance of firms listed on the New Zealand Stock Exchange (NZX) across a variety of sizes, industries, themes, and strategies. Each index is created to reflect a certain sector of the New Zealand stock market.
A particular index fluctuates (up or down) when investors buy or sell shares of a company that is a part of the S&P/NZX index. The index allows investors to watch the behaviour of the included company’s shares on a daily basis by looking at share price changes or percentage changes.
How is the S&P NZX 50 rebalanced?
The S&P/NZX 50 index is rebalanced every quarter in March, June followed by September and December with changes taking effect after the 3rd Friday of the rebalancing month when the market closes.
In the S&P/NZX New Zealand Index, rank buffers are used for insertion and deletion. If an IPO has a minimum 20 trading days of information during the quarterly revision, it may be considered for addition in the S&P/NZX 50 Index.
The share counts of the index are updated every quarter while rounding them to closest thousand.
Index addition can be done between quarters and between rebalancing dates only if a position is made available by an index deletion. Market size and liquidity are taken into account when index additions are made. An initial public offering (IPO) is only included in the index when there is a suitable vacancy and confirmed liquidity.
Acquisitions, mergers, and spin-offs, as well as suspensions and bankruptcy, might result in intra-quarter deletions between index rebalancing dates.

 Please wait processing your request...
Please wait processing your request...