What is the Therapeutic Goods Administration?
TGA, or Therapeutic Goods Administration, is the regulatory authority of Australia for therapeutic goods, including prescription medicines, medical devices, and vaccines, among others. The TGA carries out several assessments along with monitoring activities to make sure that therapeutic goods that are available in the country are of an acceptable standard. The Therapeutic Goods Administration was formed in 1989 under the jurisdiction of Commonwealth of Australia.
What do therapeutic goods include?
A therapeutic good or product is a broad term used for products that are meant to be applied in or on humans for any therapeutic reason. For instance, therapeutic purposes comprise bringing a physiological response for prevention, diagnosis, monitoring, alleviation, cure, or treatment of a disease, defect, ailment, or injury.
What is the structure of TGA?
In the Australian Government Department of Health, the TGA is part of the Health Products Regulation Group (HPRG). The HPRG includes the TGA and the ODC (Office of Drug Control).
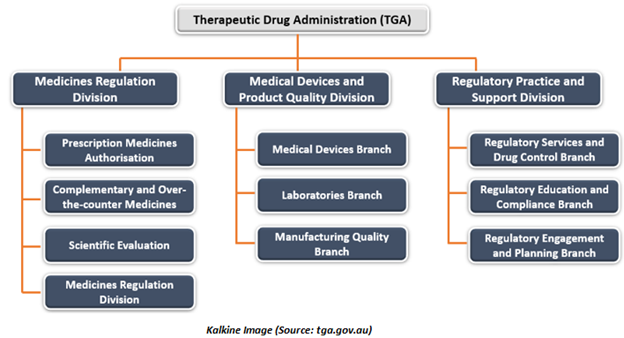
Medicines Regulation Division of the TGA evaluates applications to authorise new medicines for supply in Australia. Medicines regulation division is also accountable for monitoring drugs or therapeutic products approved for distribution in the country once they are on the market. This division includes-
- Prescription Medicines Authorisation- This section is responsible for evaluating new prescription medications, that lead to a decision of approval or rejection.
- Complementary and Over-the-counter (OTC) Medicines- Responsible for regulating over the counter medicines as well as complementary medicines, which include traditional and herbal medicines, and vitamin and mineral supplements.
- Scientific Evaluation- Accountable for approving applications to market biologicals and generic medicines in Australia.
- Pharmacovigilance and Special Access Branch- This branch supervise medicines & vaccines to make sure that they maintain a suitable level of quality, safety, and efficacy after entry into the Australian marketplace. This branch also assesses some clinical trials and special access arrangements for all types of therapeutic formulations.
Medical Devices and Product Quality Division of the TGA monitors medical devices that are approved for supply in the country and functions to make sure that Australian as well as international therapeutic goods producers meet specified standards. This division includes-
- Medical devices branch, which is responsible for evaluating medical devices, including in-vitro diagnostic tests, and monitoring them throughout their lifecycle to ensure they continue to meet an appropriate level of quality, safety, and performance.
- Laboratories branch is accountable for conducting laboratory testing, quality assessment and test procedure development in scientific disciplines like molecular biology, microbiology, immunobiology, chemistry, biochemistry, and biomaterials engineering. Moreover, the laboratories branch also contributes to post-market monitoring and the evaluation of a range of therapeutic products for market authorisation of drug.
- Manufacturing quality branch guarantees that manufacturers engaged in the production of medicines, along with tissue, blood, and cellular therapies, meet the required quality standards.
Regulatory Practice and Support Division offers operational, regulatory policy guidance as well as specific support facilities to make sure effective, best practice regulatory processes to the HPRG. The branches of this division include-
- Regulatory services and drug control branch are responsible for the Program Office of TGA, management of enquiry via the regulatory assistance division, activity-based pricing & billing, business systems help-desk, along with the coordination of internal assessments of regulatory decisions.
- Regulatory education and compliance branch look after regulatory compliance activities, including education, advertising, enforcement, and investigations into illegal and counterfeit therapeutic goods.
- Regulatory engagement and planning branch is accountable for managing engagement of shareholder with international regulators, regulatory guidance material, planning & performance reporting, media responses, coordination of technical input for Freedom of Information requests and committee support.
What is the role of the TGA?
The TGA monitors the ongoing benefits and risks of therapeutic goods once they are authorised for application. Moreover, the agency can take any action if the benefits are not realised, or additional risks become noticeable.
The probable regulatory measures are distinct from minimal intervention, like labelling modifications, to withdrawing the therapeutic good from the market.
The TGA manages an overall control via the following main processes-
- Pre-market evaluation as well as approval of registered products aimed for distribution in Australia.
- Development, maintenance, and monitoring of the system for registering any new therapeutic product.
- Licencing of producers in agreement with global standards of the good manufacturing practices (GMPs).
- Post-marketing monitoring via sampling, reporting of adverse events, surveillance activities as well as response to public enquiries.
- Assessment/review of medicine for its import and export.
Moreover, the TGA regulates the supply of-
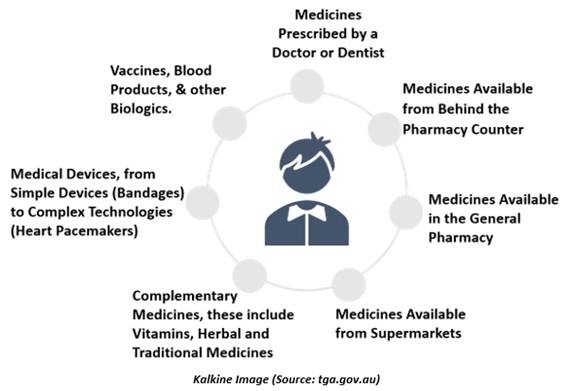
Risk management approach of the TGA to regulate therapeutic goods
The Therapeutic Goods Administration is responsible for making sure that the therapeutic goods accessible for supply in Australia are safe and appropriate for their expected objective. These include therapeutic goods Australians depend on every day, like sunscreens & vitamins through to medicines to treat severe diseases including prescription medicines, surgical implants, vaccines, and blood products.
In quintessence, this means that the agency-
- Identifies, reviews, and assesses the risks caused by any therapeutic goods.
- Applies any necessary measures for treating the risks caused by a therapeutic good.
- Monitors and analyses the risks over time.
Therapeutic goods are not free of risks completely, and the associated risks could be mild, moderate, or severe. The function of the agency is based on applying scientific along with some clinical expertise to make any decision. By this way, the agency ensures that the benefits to users outweigh any risks associated with the use of a specific therapeutic product, medical devices, or any other medicine.
For instance, some blood pressure medications might have some side effects, such as persistent cough or throat tickle. However, the associated risks by blood pressure medicine are outweighed by the advantages of lowering the chances of a stroke or heart attack. Moreover, the risk-benefit approach ensures that the medicine or products the users take are safe for their intended purpose, while still giving access to products that play an essential role in health needs.
The Therapeutic Goods Administration works closely with consumers, health professionals, industry along with international counterpart to ensure the safety of any therapeutic product or medicine.
 Please wait processing your request...
Please wait processing your request...