What do you mean by trade deficit?
Trade deficit is an economic condition when a country’s imports are greater than its exports over a given period. Trade deficit is also known as the negative or unfavourable balance of trade. Trade deficit is also the difference between the total value of a country's exports and the total value of its imports.
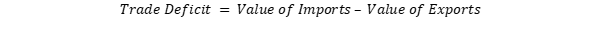
Summary
- Trade deficit is a measure of an outflow of a country’s domestic currency into foreign markets.
- Trade deficit occurs when a country is not capable enough to produce adequate goods and services to meet its domestic requirements.
- Trade deficit can also be a positive sign which indicates that the citizens of a particular country are wealthy enough to buy goods from other countries.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is trade deficit calculated?
The calculation of trade deficit is a tedious task, as it involves a large number of trade transactions pertaining to imports and exports on both capital as well as current accounts. The capital account transactions include a change in ownership of an asset or property i.e transfer of property rights to either foreigners or domestic nationals. An example can be sale or purchase of trademark rights or grant of mining rights. The current account transactions include all the transactions involved, whether it is importing and exporting goods from different foreign sources, transaction of money between countries or any international transaction between residents and non-residents. Trade deficit exists when there is a negative net amount in an international transaction account or Balance of Payment (BOP).
Both primary income payments and secondary income payments come under current account transactions.
Primary income payments refer to payments from foreign countries via direct investment (over 10% business ownership) and portfolio investment. The secondary income includes money flow between residents & non-residents, government aid and pension payments.

Image Source: © Emeraldgreen | Megapixl.com
What is the impact of trade deficit on a country’s economy?
A trade deficit can negatively impact the economic condition of a country, particularly when it depends heavily on the import of raw materials. Usually, these are countries which import consumer products on a large scale. Since, they rely heavily on import of finished products, their domestic companies lag behind as they do not manufacture these value-added products. As a result, they are entirely dependent on global commodity prices, which are often volatile. In such situations, the trade deficit can be unfavourable for a country.

Image Source: © Bswei | Megapixl.com
It is widely believed that trade deficit is not necessarily a situation to be worried about, but at times, it can be a positive sign as well. This is because it can improve the standard of living of citizens of a country through imports. They will have greater access to quality products at a favourable price. Furthermore, since these good and services are available at affordable or comparatively lower prices, they reduce the threat of inflation.
However, if continued for a long time, trade deficit can lead to the unemployment situation in a country. When a country imports more goods than what it produces domestically, then this will result in reduction of employment opportunities for the people of that country in certain industries. While on the other hand, foreign companies will hire more workforce to meet the increasing demand of their exports.
Though, trade deficit curbs inflation, however, if it persists for a longer duration, it can increase the dependence of one country on some foreign country to meet its domestic requirements. It thus weakens domestic industries in the home country. Thus, a negative balance of trade helps curb inflation, but it also makes a country more vulnerable to economic downturns. Nonetheless, trade deficit can also have an indirect impact on a country’s stock market. This can be either positive or negative. In a positive sense, it could indicate that a country is growing and thus importing more, whereas on the other hand, it could also indicate a country’s failure to sell its products in the international market.
What are the reasons for trade deficit?
There are several reasons for a trade deficit to occur. However, usually this situation arises when a country is not capable enough to produce goods as per the requirements of both the domestic market as well as for others. Trade deficit can also occur when the products being produced in a country are not liked by consumers both at home as well as foreign markets because of the stiff competition from foreign companies producing the same kind of products. Also, if a country is not rich in natural resources, for example natural gas, then it will depend on other countries for its import to fulfill its domestic requirements. Thus, trade deficit should not be considered a negative sign always as it could indicate that the country’s consumers are rich enough to buy more goods than what are being produced in their country.
With that being said, it is also true that there is a higher chance that a country will go into debt if it is consistently importing more products than exporting for a long period of time. In this way, trade deficit can adversely affect a country’s economic well-being. If the consumers are only purchasing products made by foreign companies, then the companies operating in the home country will be at a loss, and this will have an adverse impact on their stock prices. In such a situation, it is also likely that these domestic companies may want to invest in foreign stock markets due to unfavourable conditions and a lack of opportunities in the home country. If this happens, it will result in a low-performing stock market because the investors would sell the domestically acquired stocks and also increase the outflow of financial capital to foreign markets.
On the contrary, trade deficits can happen when a country is on the path of expansion and growth. It is often seen that in order to support a growing economy, many a times emerging markets witness a trade deficit to build up their infrastructure and factories. Once the infrastructure is developed and factories are built, these markets focus on their manufacturing sector to reduce their dependence on the imports.
Moreover, when a country’s economy is growing, it could experience a simultaneous increase in both the exports as well as imports. The growing economy would result in a high-performing stock market. Thus, it can be said that a country can have a trade deficit while it is growing and having a rising stock market.
What do you mean by Balance of Trade (BOT) and Balance of Payments (BOP)?
Balance of trade is the gap between the monetary value of a country’s imports and exports over a given period. Balance of Payments (BOP) keeps a record of financial transactions taking place between the citizens of a country and the international transaction over a given period of time. It is possible for a country facing a trade deficit to have a surplus in its BOP. This is because large amount of investment can offset a trade deficit.
How does trade balance influence currency fluctuation?

Image Source: © Vkoletic | Megapixl.com
Though, trade balances have a profound influence on the currency fluctuation, there are few aspects which countries can control to minimise this impact. To control currency volatility, countries can manage a portfolio of investments in international accounts. Besides, in order to keep a fixed exchange rate of their domestic currency, countries often opt for a pegged currency rate. If this is not done, then the exchange rate of a currency is considered to be floating. Currency peg is a policy wherein, a government fixes a certain fixed exchange rate of its currency as against the value of another currency or a basket of other currencies. Currency peg reduces the risk of foreign exchange and encourages international trade.
Trade deficit is just the opposite of trade surplus, which indicated an unfavourable balance of trade. In trade surplus, a country’s exports exceed its imports. Contrary to trade surplus, in trade deficit, a country’s currency demand in the global market declines. This decrease in demand of the domestic currency also lowers its value in the global market.
 Please wait processing your request...
Please wait processing your request...