What do we mean by Transfer Pricing?
Transfer pricing is the valuation of goods and services that are used by the related parties at the time of their deal or exchange. For instance, if a subsidiary company buys or sells goods to/from its holding company, the price charged is called as the transfer price. Transfer pricing is the amount paid by a division/branch/subsidiary to its legal entities for purchasing the goods and services. Legal entities may refer to the companies who are under the control of a single corporation or owned by parent company.

Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
Understanding Transfer Pricing
Transfer pricing represents the exchange price/value of goods and services, which is used by one unit to another unit of an organisation. Transfer price refers to the price which paid by one company (subsidiary) to another company (holding/sister) at the time of exchange of goods and services. For example, ABC Company is a holding company of XYZ Company. XYZ purchase goods of £10,000 from ABC Company. Here, £10,000 is called as transfer pricing.
Transfer pricing is very helpful for an organisation from taxation perspective, countries have different tax regimes related to transfer pricing which helps to reduce tax liability of an organisation. Transfer pricing is the price which is settled for buying and selling the goods and services between the different division under the within an enterprise or parent company.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the significance of Transfer Pricing?
Transfer pricing is significant to understand the allocation of expenses and profits of the subsidiaries that are located in different places and countries. It is needed to know the various functions of the management accounting and reporting. It is very difficult to the know state of different subsidiaries without the transfer pricing.
Transfer pricing is mandatory in the process of distribution of revenue and expenses of the legal entities, these legal entities can be branches, divisions, subsidiaries of a single corporation/enterprise. Transfer pricing help the management of an organisation or multinational companies in taking decision by giving an idea about the expenses and the revenue of the related enterprise.
Transfer pricing helps the management in taking decision of allocation of revenue and expenses of the companies which have different segments or a single business. The profit of a subsidiary is relying on the prices and the transactions of the inter-company. Transfer price effect also reflect on shareholders wealth as it affects the taxable income, after-tax, and free cash flow income of a company.
What are the different methodologies of transfer pricing?
The various methodologies used in transfer pricing are:

Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
- Comparable Uncontrolled Price (CUP) Method
This methodology of transfer pricing is used to make sure the exchange prices between the same organisations are comparable with the transaction price that are used for unrelated organisations. Under this methodology, Arm’s Length Price principle is used to evaluate and help in determining the value of related organisation transactions. Internal CUP and External CPU are the two methods that are used to determine Arm’s Length Price.
- Resale Price Method or Resale Minus Method
Under Resale Price Method or Resale Minus Method, resale prices are considered. It refers to the prices at which the related enterprise sells its product to the third party. After that it takes the gross margin which is found by comparing the gross margin with the unrelated transaction and then deduct from the resale price. And after this customs duty is deducted from the price of the related transaction. The final amount is treated as Arm’s Length Price or transfer pricing between the two enterprises.
- Cost Plus Method
The cost plus method is used to determine the Arm’s Length Price by considering the cost at which supplier is giving the goods and services in the related transaction. After that, the mark up will be added to the cost. Mark up here may refer to the profit of the related organisation based on their function and risk.
What are the advantages of Transfer Pricing?
Advantages of transfer pricing are given below:
- Reducing the duty costs: Transfer pricing leads to the reduction in the duty costs as it involves high tariff rates for the shipment of goods in other countries by minimal transfer prices, which results in low duty costs.
- Helps in the reduction of income and corporate taxes: Transfer price helps in reducing the income and corporate taxes of the countries, which applies high taxes by increasing the prices of goods in the countries that have lower tax rates. It helps the companies in gaining high profit margin.
What are the disadvantages of Transfer Pricing?
There are several problems and risks faced by the companies in transfer pricing:
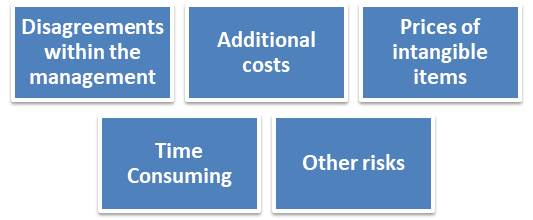
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
- Disagreements within the management: Sometimes companies face the disagreement with their management of divisions of an organisation, it may relate with the policies, pricing, and transfer.
- Additional costs: Companies have faced problems of additional cost as they need to maintain manpower, perform methodology, and proper accounting system.
- Prices of Intangible items: Companies have faced the problem in deciding the transfer price of intangible items.
- Other risks: Both sellers and buyers have performed different activities and functions, which leads to various risks related to these functions such as collection risk, credit risk, financial & currency risk, market and entrepreneurial risk, and product obsolescence risk.
- Time Consuming: Transfer pricing is a complicated and time-consuming process as it includes different methodologies to determine the price.
 Please wait processing your request...
Please wait processing your request...