What is a vaccine?
A vaccine is a biological product injected to stimulate the creation of antibodies or toxins or lymphocytes or microorganisms to provide prevention against diseases. A vaccine stimulates the immune system to raid a particular harmful agent of illness. In active immunity, the antibodies remain sensitised and ensure that the agent does not enter the body again.
Vaccines can be administered orally, through injection or through nasal. A positive response has been observed when the vaccine is administered through nasal or gut lining.
Summary Points

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How does the vaccine work?
Different types of cells make up the immune system, and these cells help the immune system to gain a defensive mechanism against the invaders and remove them. However, the current immune system cannot recognise the harmful invaders.
Vaccination helps the immune system increase its capability to recognise the invaders that are harmful to the body. Vaccination creates antibodies that, in a way, ‘teach’ the immune cell to detect the invaders, which can be the cause of infections. Once vaccinated, the antibodies can induce response actively in future as well.
What is the composition of a vaccine?
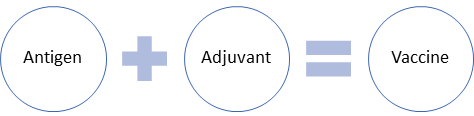
A vaccine is generally composed of two parts, namely, antigen and adjuvant.
- Antigen: This part of the vaccine helps the body recognise the agents that can attack the body.
- Adjuvant:After recognition, the adjuvant tells the body that invasion has taken place, which can be dangerous for the body or cause infection. In response, the body’s immunity becomes strong and protects the body from the infection.
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media Pty Ltd
How is protection achieved after vaccination?
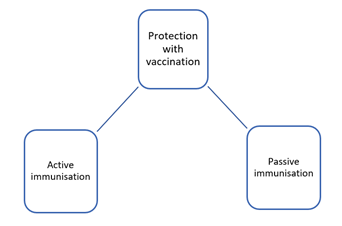
There are two different ways in which protection is generated.
- Active immunisation– It triggers the body to produce antibodies on their own against the invaders to which they are exposed to. Long-term protection is achieved against a particular disease or infection. It is achieved through two processes, that is, vaccination or natural immunity. Natural immunity is achieved when one’s body is exposed to the infection—for example, chickenpox.
- Passive immunisation– It extends protection for a short period. The antibodies are injected into the body as the human body is incapable of making it independently. It can be transferred through breastfeeding or artificially.
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media Pty Ltd
Are vaccines safe?
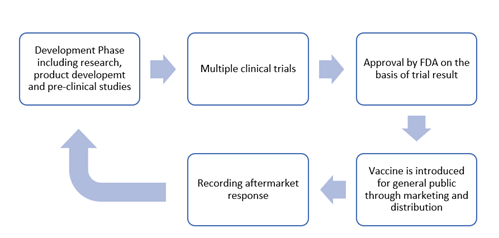
Before injecting the vaccine to the general public, vaccines are tested through multiple rounds of research, examination and study. Therefore, vaccines are considered safe by health organisations.
Extensive researches have projected that vaccination procedures are safe. In case a side effect is observed, it is generally mild.
Individuals can be exposed to a range of diseases if vaccination is not done. In comparison to the side effect of vaccines, exposure to illness or infection can be more deadly.
However, Vaccines are composed of many different components, so before taking vaccination, the allergic reactions need to be checked with the physicians.
Vaccination Process, Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media Pty Ltd
How effective are vaccines?
The effectiveness of the vaccine is dependent upon the type of vaccine and the invaders it is targeting. No vaccine has shown a 100% success rate.
For example, it has been observed that flu vaccines are able to reduce the infection rate by 40 – 60 per cent. On the other hand, the measles vaccine have showed an efficacy of reducing the infection by 98%. As per WHO (World Health Organization), most childhood vaccines have an effectiveness rate of 85 – 95 per cent.
What should you know about the COVID-19 vaccine?
The COVID-19 vaccine is being developed to build immunity in human beings against the coronavirus. Before entering the market, COVID – 19 vaccine received FDA approval after it has undergone several clinical trials. Since it takes several months to complete the procedure, FDA had given authorisation for the emergency use of the vaccine.
Pfizer and modern COVID-19 vaccines showed above 94% effectiveness in preventing the symptoms of the COVID-19 virus. Two doses of the vaccine are given to non-infected people above the age of 18 as of now.
Are the COVID – 19 vaccines available, efficient against the variants of coronavirus?
The researchers presented the view that the vaccine is not adequate for the variants of coronavirus. However, protection is extended to some extent. The manufacturers and researchers are creating dosages that can develop antibodies against the mutated virus.
However, even after getting the vaccination, a person can get infected with the virus. The vaccine only helps build immunity, and it can take up to a week for building strong immunity.
 Please wait processing your request...
Please wait processing your request...