What is valuation analysis?
The process of defining a value to a company or its stock is termed valuation analysis. There are many methods for conducting such an analysis, which may also be partially subjective. Analysts use various approaches for conducting a valuation analysis. These may include assessing market multiples of comparable companies, discounting its cash flows, or even forming financial projections.
Highlights
- Valuation analysis is the technique used to estimate the value of a business or its security.
- The valuation may be based on the present value (PV) of all future cash flows or the value of a model company or transaction from the same industry.
- The resulting value can be a single figure depicting business value or a range of values depending on numerous scenarios considered.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are the main methods used in valuation analysis?
To value a firm as a going concern, there are mainly three valuation analysis techniques that industry analysts use:
- DCF analysis,
- Comparable company analysis, and
- Precedent transactions.
Investment banks commonly use these methods of valuation. The use of these techniques is also evident in business mergers & acquisitions (M & M&A), leveraged buyouts (LBO), and other critical financial transactions.
The comparable company analysis and the precedent transactions method is also called the market approach. It is so because these methods form a relative valuation and are frequently used by industries. Meanwhile, the discounted cash flow (DCF) approach is a form of intrinsic valuation which is detailed and thorough. It even includes valuation modelling for the firm.

Source: © Pichetw | Megapixl.com
What is DCF analysis method of valuation?
Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) method is an intrinsic value approach. It is used by analysts to forecasts the business’ unlevered free cash flows into the future. The cash flows are then discounted back to the current date using the firm’s Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC). A DCF analysis requires analysts to build an excel model and requires a detailed analysis. It also uses estimates and assumptions. However, it often results in the most accurate valuations. The DCF model allows the analyst to forecast values based on scenarios and sensitivity analysis. For larger businesses, it is commonly a sum-of-the-parts analysis. All the different business units are modelled separately and added together.
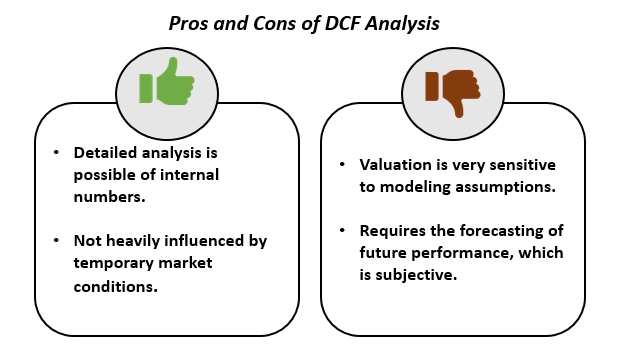
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
What is comparable company analysis?
Comparable company analysis is a relative valuation, also known as the trading multiple methods or peer analysis technique. The method compares the current value of a business to that of similar businesses. For this, it utilises trading multiples like P/E, EV/EBITDA, or other ratios. It is prevalent to use multiples of EBITDA for valuation. It provides a value to a firm that is based on what other comparable firms are currently worth. It is very easy to calculate method.
Example-
If an analyst knows that company XY Paints trades at a 10-times P/E ratio, he can use this data to compute the value of its peers. Suppose its peer YL paints report earnings of AU$2.50 per share, then the company YL’s stock must be worth $25.00 per share. It is arrived at by multiplying the earnings of YL with the PE multiple of XY. Here the analyst assumes that both the companies have similar attributes as they are peers.
What is precedent transactions approach of valuation?
The precedent transactions analysis is another method. Here, the firm being valued is compared to other businesses that have recently been sold or acquired in the same industry. This method is helpful for M&A transactions. But the transactions considered can quickly become a thing of the past. They may not any longer remain reflective of the current market.
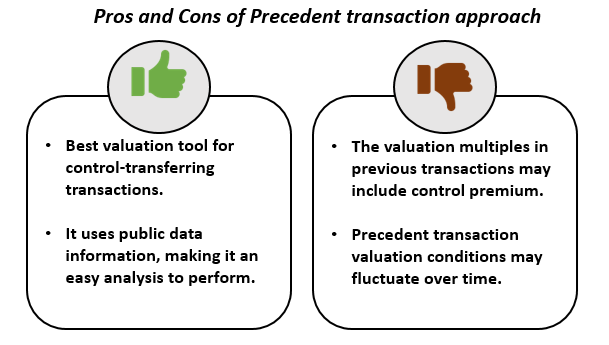
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
Why is valuation analysis used?
The result from the valuation analysis can either be a single number or a range of numbers. It depends on the method used by the analyst. Though it does not give an expected result, valuation analysis is still essential for investors to estimate intrinsic values. It helps them make informed choices for capital deployment. Valuation analysis is a valuable tool for comparing companies within a sector or for estimating a return on investment over a given period. Given below are few reasons to perform a business valuation.
- During litigations on a company, it is essential to determine the value of its business, the valuation acts as proof of the company’s worth. Any damages claimed in the litigation are based on the actual worth of the firm.
- If there is a plan to sell off a business unit, it is advised that a company first assign a value to it then come up with an exit strategy. A valuation will keep the business with a sale price expectation. It will also ensure that correct information on fair market value is taken to prevent capital loss caused by inaccuracies.
- Real business value is what the buyers are willing to pay. A reasonable business valuation looks at market conditions, the potential income of the business, etc., to ensure investment is viable.
- Setting a valuation helps in Bargaining. The asking price must be attractive to prospective purchasers, and the seller must get the worth of his business.
- It helps in strategic planning. The actual value of assets based on the current valuation of the business will give good information to make better business decisions.
- Objective valuation is helpful in negotiations with banks for funding.
 Please wait processing your request...
Please wait processing your request...