What is Well Casing?
Well Casing is the process of supporting the walls of a newly drilled borehole from collapsing by inserting a larger diameter pipe into the borehole. The pipe is assembled, inserted, and cemented into a freshly drilled section of a wellbore to support the walls of the hole from collapse. The strength of pipe undertaken for the casing is chosen in such a way so that it can hold the outside formation pressure to avoid it from collapsing. At the same time the casing pipe should also be capable of withstanding the inside pressure exerted by drilling mud.
What is the process of casing a well?
The casing is a typical hollow steel pipe that is lined inside a wellbore. The casing process is carried out in phases depending on the depth of a well. Each section of the casing is known as casing string. The internal diameter of the casing pipe is smaller as compared to the wellbore's diameter. The casing of a well is executed in a telescopic manner. The process is started with the casing of the largest diameter section first, followed by sections of smaller diameters.
The casing is run into the wellbore from the rig floor with the help of casing elevators. The casing pipe is then hanged on the casing hangers with the help of slips or threads. The hangers are located at the top of a well. Apart from this, casing centralisers are fitted at the outer surface of the casing for the hole-concentric placement of the casing.
After the proper placement of the casing into the wellbore, cement slurry is pumped through the casing to fill the annular space present between the casing and borehole. After some time, when the cement gets set, it sticks to the borehole walls and the casing, providing strength to the casing and support to the well.
What are the different functions of Casing?
Casings have a wide variety of functions; some of the important functions are stated below:
- Casings provide support to weak, fractured, and vulnerable formations, which can collapse into the well and complicate the drilling process.
- Casings are also helpful to stop contamination of freshwater zones with drilling mud while drilling.
- Casings also provide support to surface equipment like production trees and blow-out preventers. BOPs are very helpful for controlling the well when a well encounters a kick.
- Casings also allow the installation of artificial lifting systems which are used for the enhanced recovery of hydrocarbons from the reservoir.
- The use of casing helps the operator to get a uniform cross-sectional borehole, making all the operation easy.
Summary
- Well Casing is the process of supporting the walls of a newly drilled borehole from collapsing by introducing a large circular cross-sectional pipe into the borehole.
- Casing strings are inserted and cemented into the wellbore in a phased manner which provides support to the walls of the borehole.
- The diameter, size, and strength of the casing are chosen based on the depth and cross-section of the wellbore.
FAQs:
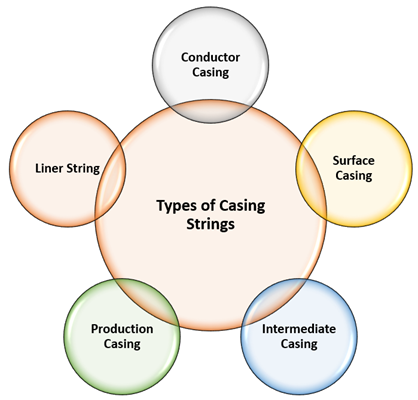
What are the different types of Casing Strings?
There are five basic types of casing strings that are used for the casing of an oil and gas well.
Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media Pty Ltd
- Conductor Casing: It is the largest diameter casing that is run into a borehole. Conductor casing is introduced at 100 feet below the ground level. The main objective of the conductor casing is to isolate the unconsolidated formations which are present near the surface to enter into the wellbore. The diameter of the conductor casing ranges from 16 to 20 inches in onshore and 30 to 42 inches in offshore.
- Surface Casing: Surface Casing is the next casing that is introduced into the wellbore. The length of the casing ranges from a few hundred feet to 2,000 feet. The diameter of the surface casing is smaller than the conductor casing. The main objective of this casing is to seal off the freshwater zones. The casing also provides support to blow out the preventer.
- Intermediate Casing: It is the longest casing string that is run into the wellbore. The main objective of this casing is to minimize the hazards that may come due to high pressured formations and risk the drilling process. The number of intermediate casings runs depends on the problems which are encountered while drilling the well.
- Production Casing: Production casing is run above the producing zone. The main objective of production casing is to isolate the producing zone from other water-bearing sands. It is the deepest section of the casing of a well.
- Liner String: Liners are run from the bottom of another casing to the open well area. Liners are hanged with the help of hangers instead of cementation. Liners consist of slips that can be activated mechanically or hydraulically.
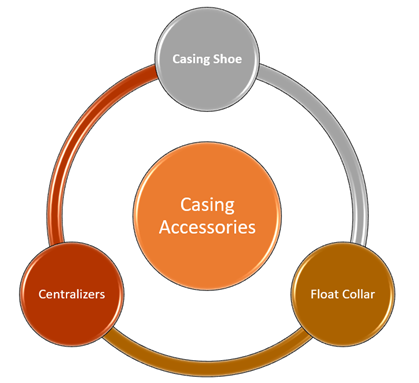
What are different accessories used with casing?
There are various types of accessories used with casing which are used in oil or gas well casing. Some of the most useful accessories are listed below:
Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media Pty Ltd
- Casing Shoe: The casing shoe is run at the first joint of the casing. The two main types of casing shoes are guide show and float shoe.
- Float Collar: It is a type of sub that is placed between the two first joints. The float collar prevents fluid to flow back into the casing while running. The float collar also stops the U-tube effect before the hardening of the cement.
- Centralisers: Centralizers are placed around the casing joints. They are used to centrally position the casing into the wellbore. They are two types of casing hangers that are Mandreal type and Slip type. Mandreal type is screwed on the top of the casing string while slip type is wrapped around the casing body.
 Please wait processing your request...
Please wait processing your request...