What is Well Testing?

Source: © Bashta | Megapixl.com
Well testing is a process of determining the properties of a reservoir that contains hydrocarbons. The technique provides detailed information about the condition of the well. The primary objective of well testing is to understand the reservoir capacity to produce hydrocarbons ,including natural gas and crude oil.
The technique determines reservoir pressure, fluid properties, drawdown pressure, productivity index, permeability, formation damage, and a lot of other information. It allows the company to draw some fluid samples from the reservoir to determine the properties of hydrocarbons. The properties of fluids present in the reservoir are useful during the well completion stage. Well testing requires high-end technology, planning, and execution to rightly gather data for appropriate calculations and estimations.
When does a well testing operation is performed?
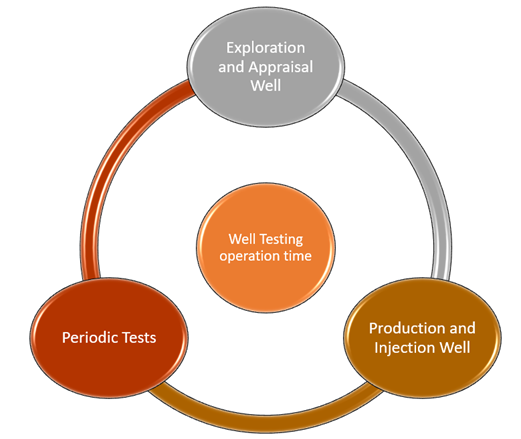
Well testing measures flow rates and pressure of hydrocarbons at the surface with the help of a gauge fitted on the downhole side of the well. Well testing is the process of obtaining pressure and flow data with the help of special techniques and tools. The technique can be applied during exploration, producing and injection wells. Periodic well tests are also performed on wells to understand a well's performance. Let us look at the advantages of performing a well test on both types of wells.
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
- Exploration and Appraisal Well: In exploration and appraisal, well testing helps confirm the hydrocarbon discovery. The technique also helps determine the well productivity, hydraulic connectivity, reservoir boundaries, reservoir heterogeneity, initial pressure, and a lot more information. The activity also draws some samples from the well that can be used to perform PVT analysis in the laboratory to understand hydrocarbon nature and test the sand production.
- Production and Injection Well: In production and injection well, baseline tests, including PBU/PFO tests, are performed on the well right after the commencement of production, giving information about the initial reservoir pressure conditions. In addition to that, the interpretation of well test data also gives information about average permeability thickness and initial skin post drilling and completion of the well. The initial test results can be used as the reference that can be used for comparison purposes for the tests performed at a later stage.
- Periodic Tests: Periodic tests are performed on wells with the help of downhole gauges to monitor well properties like permeability thickness and formation damage over time. The technique helps to foresee a water breakthrough. A deviation in a well's performance can be a result of wellbore damage or pressure support. The problem can be diagnosed by the combination of production logging and well testing, and appropriate well treatment can be planned to enhance the production life of a well.
Summary
- Well testing is a process of determining reservoir properties containing hydrocarbons that provides detailed information about the state of the well.
- Well testing can be performed on various stages of a life cycle of a well like exploratory phase, production phase, and periodic tests.
- Well testing requires high-end technology, planning, and execution to rightly gather data for appropriate calculations and estimations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
What are the different types of Well Testing?
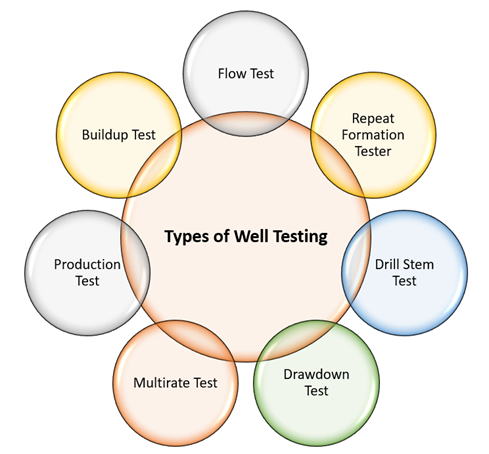
There are several types of well testing techniques used in the industry, the most prominent techniques are Flow test, RFT, Drawdown test, Drill Stem test, Production test, Multirate test, Buildup test. Let us discuss them briefly one by one.
Source: Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media
- Flow Test: A flow test is used to determine the presence of movable hydrocarbon in a reservoir and its potential productivity. A Drill Stem Test (DST) is performed in an open hole to draw fluid samples from the reservoir. The test also helps to obtain productivity, bottom-hole pressure measurements, and short-term flow. Other flow tests like multi-point tests and single-point tests are performed on cased holes to determine initial or average reservoir pressure and gas well deliverability.
- RFT: The repeat Formation Tester test can be performed either open or closed well to check pressure equilibrium. Testing tools like MDT or RFT can be run at the desired depth to get the results.
- Drill Stem Test: Drill Stem Tests are performed on newly developed reservoirs before completions or fully insulating the production facilities. The test is performed with the help of an on-site drilling rig.
- Drawdown Test: A drawdown test is performed at a constant production rate by closing the well for a period sufficient to allow pressure stabilization through the formation. The test can be performed in new wells with no production loss. In addition to that, the test can also help to determine reservoir size.
- Multirate Test: Multirate tests are performed on well with a series of variable flow rates to determine deliverability, especially in gas wells. The test also accounts for negligible production loss.
- Production Test: A production test is much similar to a drawdown test where the test is performed at a constant production rate. The primary difference between both the test is time. A production test is usually run for a longer period than a drawdown test.
- Buildup Test: A buildup test is performed to determine bottom hole pressure after the shut-in of a producing well. The test helps to obtain skin effect, permeability thickness, and well flow capacity.
What are the advantages of well testing?
There are numerous advantages of well testing. Let us have a look at the most important applications of a well-testing technique.
- Well Testing can be used as an important tool for quality control rate measurement.
- Well testing can also help to detect a liquid breakout in a condensate well or a gas breakout in an oil well.
- Shut-ins on water injectors can also help to determine injectivity and frac size over time.
- It can also be used to identify thermally induced fractures.
- Well testing can be used to analyze the impact of water quality on well performance.
 Please wait processing your request...
Please wait processing your request...