Artisanal and small-scale mining (ASM) is a mining practice that requires labour-intensive mineral extraction and processing using minimal modern machines. Artisanal and small-scale mining (ASM) provides essential livelihood to more than 150 million people globally.
The sector has recently grabbed the interest of international organisations and government institutions because of its strong influence on the nation's economy, environment and society.

Source: © Belenbmproyectos | Megapixl.com
Various minerals, including gold, diamond, gemstones, cobalt, coal, etc., are mined by artisanal activities.
What are the drivers of ASM?
There are numerous factors responsible for ASM activities. However, poverty is the biggest driver as it helps the poor earn their livelihood in largely rural communities. ASM activities provide income for their livelihood; however, they remain trapped in these activities because of the lack of alternate earning sources. Because of poverty and lack of technical expertise, the productivity of the process remains low. The absence of good working conditions coupled with lower income leads to HSE related issue.
What is the distribution of ASM in the world?
Since poverty is the main driver of ASM, the practice is common in less developed regions. Though ASM activities are carried out in more than 80 countries globally, the leading regions are the Caribbean, African, and Latin American regions. Pacific regions and East Asia are also among the leading regions where these practices are followed.
What is the importance of ASM in global mineral supply?
ASM has a wide role in sourcing geological materials and valuable minerals that are processed further to transform them into the products we use in our daily lives, like jewellery, automobile parts, electronic gadgets, etc. There is a vast dependence of western countries for the raw materials on the developing regions like Africa, South America and Oceana. ASM activities are legal in few countries.
ASM activities account for around 20 per cent of the world's annual supply of metals and minerals. The most common mineral mined through ASM is gold which contributes around 20 per cent of the world's total supply.
Around eighty per cent of sapphires and 20 per cent of the world's diamonds come through ASM activities. The world's 25 per cent of total tantalum production comes as a result of ASM activity. Sand, limestone and phosphate are small scale artisanal mining products that are usually referred to as Low-Value Minerals and Materials (LVMM).
Summary
- Artisanal and small-scale mining (ASM) is a low technology-based and labour-intensive mineral extraction and processing practice.
- There are numerous factors that are responsible for ASM activities; however, poverty is the main driver of these activities.
- The sector provides livelihood to more than 150 million people and is carried out in more than 80 countries worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
What are the various types of human rights challenges of the ASM sector?
There are various human rights challenges of the ASM sector. Let us have a brief look at the following challenges:
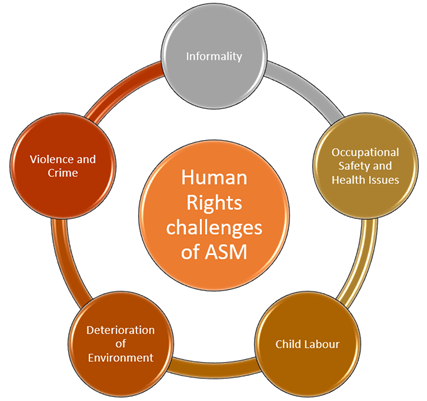
Copyright © 2021 Kalkine Media Pty Ltd
- Informality: The biggest challenge of the ASM sector is informality, which forces miners to work in poor working conditions. The miners can't fight for their basic rights in the absence of formalisation of the sector.
- Occupational Safety and Health Issues: Since the sector is mostly run on an informal basis worldwide, no proper regulations or labour laws are applicable to artisanal miners. The adverse working conditions, exposure to toxic chemicals like mercury deteriorate workers' health, lead to chronic disease and early deaths of miners.
- Child Labour: Despite the globally circulated strict guidelines for child labours, children working in the ASM sector perform various tasks risking their health.
- Deterioration of Environment: Since ASM miners usually don't have a license for the extraction of minerals, the mining is undertaken in an unprofessional manner, resulting in an adverse impact on the environment. Mineral extraction destroys animal habitats, topsoil, vegetation, water quality etc.
- Violence and Crime: Violence and crime are an integral part of the ASM. Since the whole sector is run illegally, it is backed and run by local groups with the support of illegal mineral importers of the world.
How can the ASM sector be formalised?
Despite the existence of legal guidelines and frameworks, most of the ASM activities around the globe are carried out illegally without any type of permit or licenses. However, the formalisation of the sector will improve the working conditions for the miners. It will also help to reduce the negative environmental effects. Formalisation can also come up as a significant step to creating substantial job opportunities and revenue generation for the government.
Streamlining the licensing policy with the involvement of government institutions, proper allotment of mining rights and providing equipment support for the mining activities can help streamline and formalise the sector.
Better enforcement of laws related to ASM and education of those laws can help the miners regain their working rights. The commencement of an ASM association can also help the miners to develop and strengthen the community to incorporate the best practices into the sector by sharing the experiences of each other. These associations will also help the government and policymakers to build a knowledge-sharing forum and begin the consultation of specific matters.
 Please wait processing your request...
Please wait processing your request...