What is a remittance?
Remittance refers to a sum of money sent from one party to another. This term is usually referred to indicate payments to and from abroad. Some of these payments include money transferred to students abroad, money sent by children from abroad to their parents residing in another country, or they can also be business transactions.
The word remittance is derived from the word “remit” which means to send back. Remittances can be sent via wire transfer, electronic payment system, mail, draft or even cheque. Remittances have become increasingly popular due to the increased amount of connectivity in the world leading more people to go abroad.
Remittances are generally fast, given the current advancements in technology. Most channels used to transfer money across the border require a certain amount of fees to be paid.
Summary
- Remittances are overseas monetary payments made from one party to another.
- The term is derived from the word “remit” which means to send back.
- With increasing global migration, the number of remittances has also increased worldwide.
- Most remittance channels may require specific fees to be paid to complete the transaction.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why are remittances gaining popularity?
Two key forces are leading to the popularity of remittances in the current age:
- Migration: With increases global opportunities, it has become easier for people to look for career and education prospects outside of their home country. Adding to that, international transport has become more accessible and more affordable than it was in the past. Therefore, more people are now choosing to live and work in foreign countries.
- Integrated businesses: Increased global integration is visible in how businesses conduct their operations. With the help of internet, it is possible for a company set up in a country to procure clients from another country. Such cross-border operations require money to be transferred frequently. Thus, number of remittances have seen a sharp uptick in the past decade.

Image Source: © Josepalbert13 | Megapixl.com
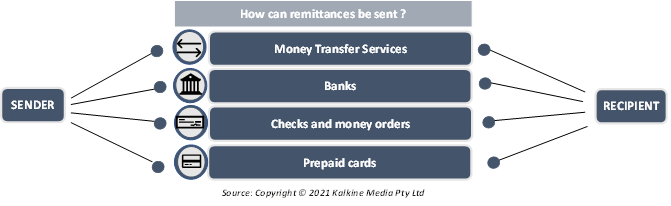
How can remittances be sent?
Most of the available options include a fee that must be paid for the international transfer. This fee can be directly charged as a service fee, or it may also be built into the exchange rate that the remittance provider takes. The following methods allow remittances to be sent in an easy manner:

Image Source: © Dimoza | Megapixl.com
- Money Transfer Services: There are specialized services that allow individuals staying abroad to send money overseas. There are various options in this category. Online transfer can happen by simply opening an account and entering the details of the recipient. This type of payment can be made using a credit card or a debit card, though each has a different fee attached to it. Typically credit cards have a higher fee associated with them.
The second method is to transfer in person via cash. This involves paying cash to agents who can then transfer the money via online transfer services. Some of the offline transfer facilities also have self-service options available.
- Banks: This is the easiest and fastest way to send money overseas. Banks have partnerships with other foreign banks, retail stores or some other select locations. This service can be simply availed by enquiring the bank about the options they provide.
- Checks and money orders: For the technologically challenged individuals who are not familiar with online methods, transactions on paper are a good option. This option may take much longer than other methods and may require the recipient to have a bank account in the foreign country where the money is being sent. Thus, the sender must first enquire about the recipient’s bank details.
- Prepaid cards: This is a relatively easier option than transferring money directly. This is an indirect method under which the sender puts money into a card which can then be used in the foreign country to make purchases. A major drawback of this option is that it involves a huge fee. Additionally, the card must be physically carried to the foreign country. So, the recipient must be first present with the sender to collect the card and then leave for abroad or someone must act as a mediator between the two.
What are specific terms associated with remittance?
- Remittance advice: Remittance advice is a document that a customer sends to a seller with the intent to inform the latter that an invoice has been paid. This type of document may not be mandatory always but is considered a courtesy. However, due to the non-mandatory nature of the document, it is becoming less and less frequent.
- Remittance address: This is the address of the recipient and is often referred to as the remit-to address. The correct address must be known so that the money can be sent without fail and without any delays.
- Remittance float: This refers to the time taken for just the payment process to finish. This does not include the time taken for the sender to pay the money. However, once the money is transferred overseas then the time taken for the payment to process into the recipient’s account is known as remittance float.
What is the importance of remittances?
Remittances are not a direct component of Gross Domestic Product or GDP. Remittances are not directly added to GDP as they are only a one-way transfer. This means that no corresponding output is produced in exchange for a remittance sent to or obtained from abroad.
However, in most developing countries, they form a sizeable part of the national income by contributing to household consumption. So, the country where the remittance recipient resides sees a growth in GDP when the recipient uses the money towards consumption.
The only drawback of remittances is that while they prevent countries from taking loans from abroad, they might make countries dependent on outside money. This can hamper domestic growth and can create a lack of sustainable economies in the home country.
 CA
CA  AU
AU UK
UK US
US NZ
NZ Please wait processing your request...
Please wait processing your request...